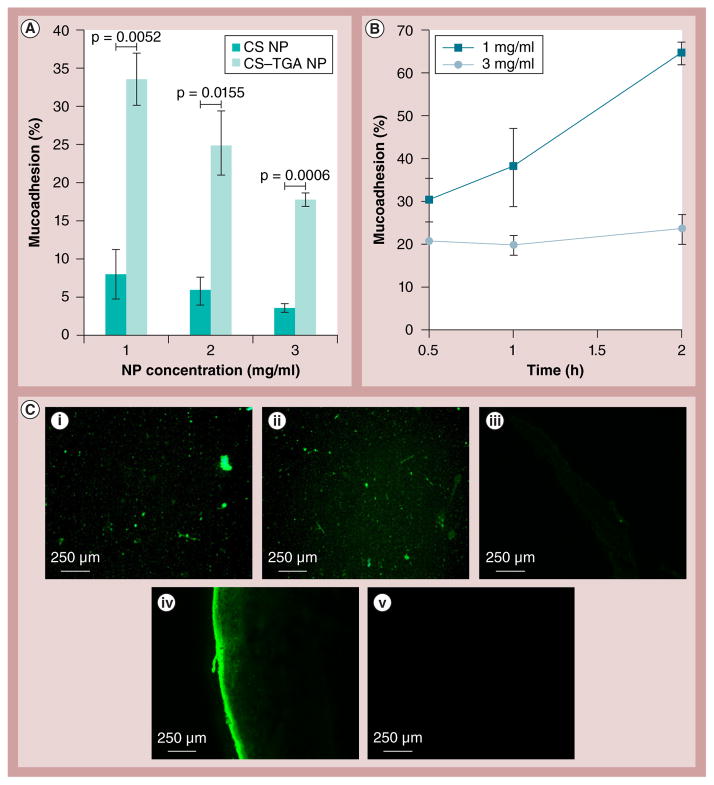
Figure 8. Results of the nanoparticle mucoadhesion studies.
(A) Concentration-dependent percentage mucoadhesion by infusion method; and (B) time-dependent percentage mucoadhesion by immersion method. (C,i) Fluorescence microcopy of fluorescein isothiocyanate-CS NPs suspension (3 mg/ml) and (C,ii) fluorescein isothiocyanate-CS–TGA NPs suspension (3 mg/ml). Thin sections of porcine vaginal tissue treated with (C,iii) suspension A, (C,iv) suspension B and (C,v) media. NPs are prepared with a concentration of CS–TGA conjugate (w/v%) of 1, a sodium tripolyphosphate/chitosan–thioglycolic acid conjugate weight ratio of 0.96 and a drug/chitosan–thioglycolic acid conjugate weight ratio of −1. Data are shown as mean ± the standard error of the mean (n = 3). CS: Chitosan ; CS–TGA: Chitosan–thioglycolic acid conjugate; NP: Nanoparticle.