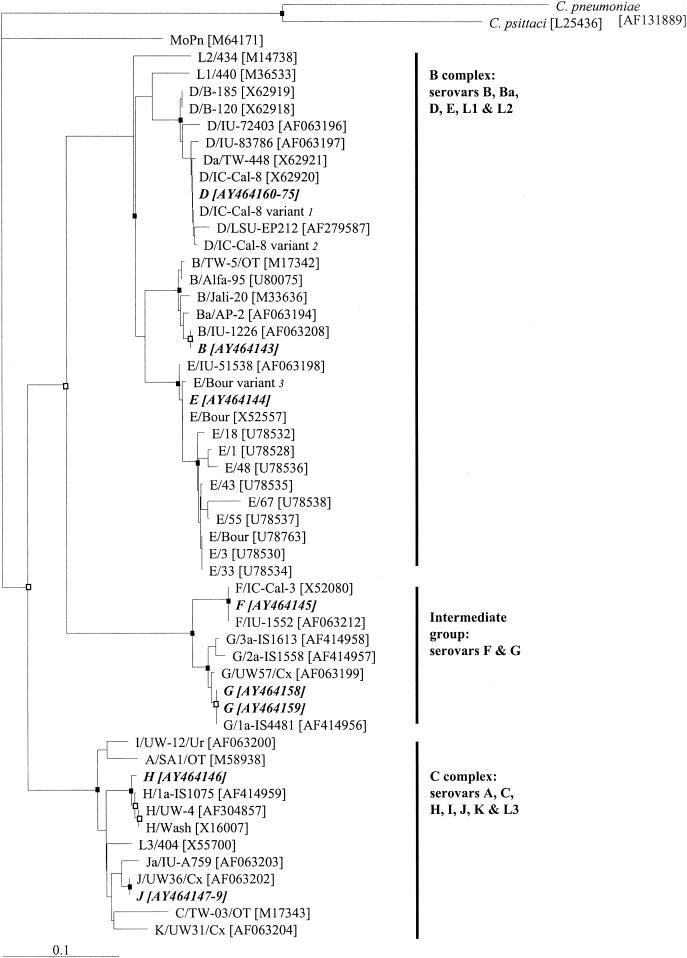
FIG. 1.
Dendrogram illustrating relationships of deduced amino acid sequences of C. trachomaits omp1 genes recovered from men in Melbourne male-only saunas. The dendrogram was generated by use of the Jones-Taylor-Thornton model and the neighbor-joining method with the PROTDIST program in PHYLIP (9). Each branch terminus contains the names and the GenBank accession numbers (in brackets) of the MOMP sequences. The deduced MOMP sequences from this study are shown in boldface italicized text and are assigned the same letter for the corresponding serovar. The different clusters of C. trachomatis serovars (18, 33, 37) are indicated on the right. C. pneumoniae and C. psittaci strains were used as the outgroup to root the dendrogram. Bootstrap values were obtained from a consensus tree based on 1,000 randomly generated data sets with jumbled sequence addition. Nodes recovered in 90% or more of the 1,000 bootstrap dendrograms are indicated by a closed box, those recovered in 70 to 89% of the 1,000 bootstrap dendrograms are indicated by open boxes, and those recovered in less than 70% of the 1,000 bootstrap dendrograms have no symbol. Bar, 0.10 inferred amino acid changes per position. Notes: 1, the D/IC-Cal-8 variant was described by Jurstrand et al. (17), with a difference of R→H at position 72 in comparison to the MOMP sequence of D/IC-Cal-8 (GenBank accession no. X62920); 2, the D/IC-Cal-8 variant was described by Jurstrand et al. (17), with a difference of A→T at position 326 in comparison to the MOMP sequence of D/IC-Cal-8 (GenBank accession no. X62920); 3, the E/Bour variant was described by Jurstrand et al. (17), with a difference of A→T at position 333 in comparison to the MOMP sequence of E/Bour (GenBank accession no. X52557).