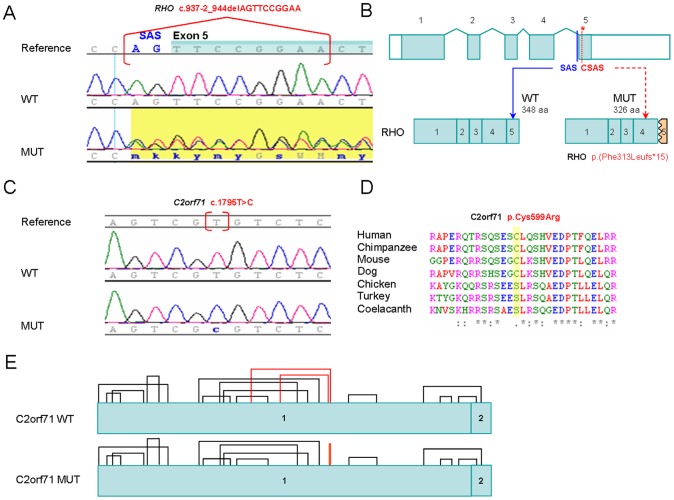
Figure 2. Novel pathogenic variants identified in this study.
A) Chromatograms of wild type (WT) RHO DNA sequence (NM_000539.3) and RP subject (MUT) showing the heterozygous mutation c.937-2_944delAGTTCCGGAA. SAS: Splice Acceptor Site. Exon 5 is highlighted in blue. B) The RHO gene structure is composed of 5 exons that are indicated as filled boxes while 5′ and 3′ UTRs are shown as open boxes. The canonical SAS of exon 5 is in blue and the predicted cryptic SAS (CSAS) is in red and indicated with an asterisk. The WT protein product (left) has 348 aminoacids (aa) while the predicted mutant product (MUT) only 326 aa. C) Chromatograms of WT C2orf71 (NM_001029883.2) DNA sequence and RP subject (MUT) showing the homozygous mutation c.1795T>C. D) Alignment of C2orf71 orthologous protein sequences showing conservation of the mutated residue p.Cys599Arg among mammals. E) Prediction of disulfide bonds formation for WT and mutant (MUT) C2orf71 proteins. According to the prediction, in the mutant protein structure, two of the disulfide bonds have been disrupted while a new one has been created. The disulfide bonds altered are in red.