FIG 1.
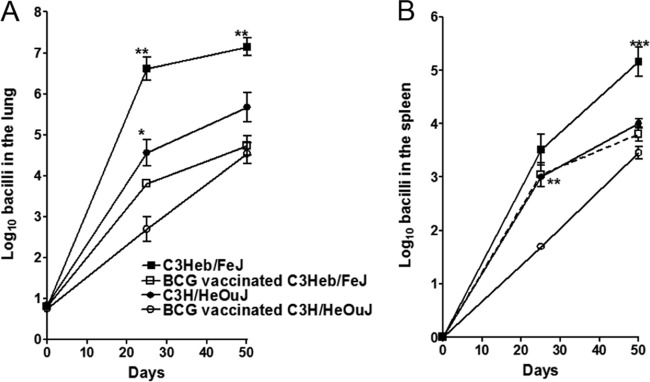
BCG-induced protection is lost in infected C3H/HeOuJ but not C3Heb/FeJ mice. Shown are bacterial counts in the lungs (A) and spleens (B) of control C3Heb/FeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice as well as BCG-vaccinated immune C3Heb/FeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice infected with a low-dose aerosol of M. tuberculosis W-Beijing strain SA161. CFU were determined on days 25 and 50 after infection by plating serial dilutions of organ homogenates onto nutrient 7H11 agar and counting CFU after 3 weeks of incubation at 37°C. For both murine strains, BCG vaccination resulted in a reduced bacterial burden at day 25 in comparison to the bacterial burden in nonvaccinated animals. However, protection in both the lungs and spleens of C3H/HeOuJ mice was lost at day 50 after infection. C3Heb/FeJ mice demonstrated strong BCG vaccine efficacy throughout infection. Results represent the average (n = 5) bacterial loads in each group and are expressed as log10 CFU (±SEM). *, P < 0.050; **, P < 0.010; ***, P < 0.001 (determined by ANOVA and the Tukey test).
