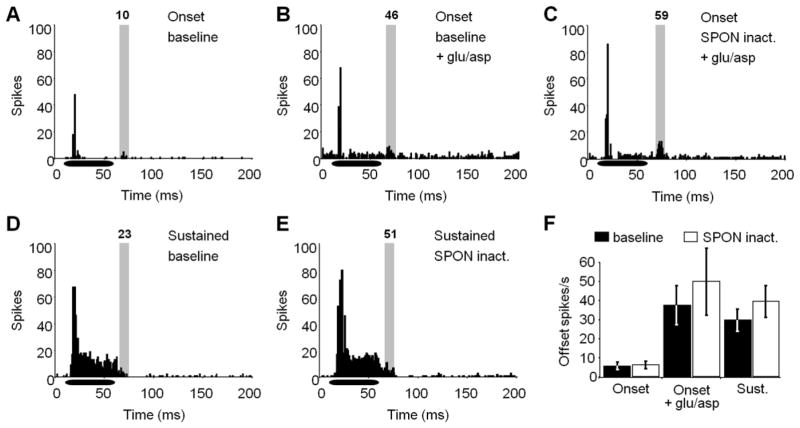
Figure 4. IC neuron responses to pure tones are unaltered during SPON inactivation.
(A) A representative onset response to a CF pure tone is shown for the baseline condition. To get a better indication of whether SPON input is manifest following the stimulus offset, overall spiking activity was elevated with iontophoretic application of glutamate and aspartate for baseline (B) and SPON inactivation (C) conditions. A small increase in spiking in the offset analysis window (shaded area) was observed during SPON inactivation. (D) Sustained IC units exhibited high levels of spiking throughout the stimulus presentation and extending into the analysis window. (E) The sustained unit in D showed an increase in spiking rate in the analysis window during SPON inactivation. (F) For onset neurons, spiking activity remained low in the offset analysis window before and during SPON inactivation. When glutamate and aspartate were applied by iontophoresis, SPON inactivation caused an increase in spiking, although the change was not significant (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p > 0.05). The average spiking rate was also higher during SPON inactivation for sustained units, but this difference was also not statistically significant. Spike counts are displayed at the top of each analysis window. Horizontal bars represent the location of the stimulus within the recording window. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means.