FIG 1.
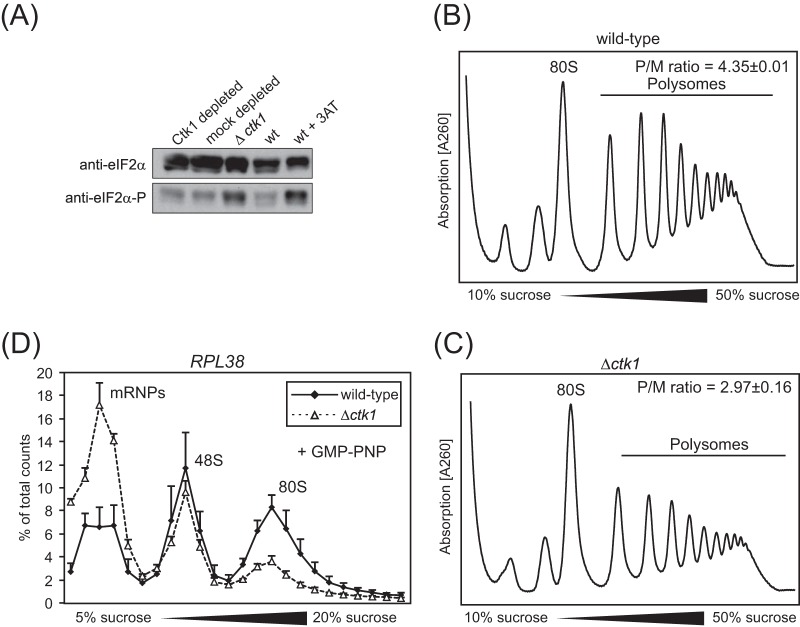
Impaired translation in Ctk1-depleted cells is not due to an overall stress defect as in Δctk1 cells. (A) Upon amino acid starvation (30) and some other stress conditions, e.g., peroxide stress (31, 32), eIF2α is phosphorylated, leading to a decrease in ternary complex (TC) formation and thus inhibition of translation initiation (30). Western blotting of Δctk1 and Ctk1- and mock-depleted extracts against total eIF2α and phosphorylated eIF2α (eIF2α-P) reveals that the phosphorylated form of eIF2α is increased in Δctk1 cells and cells treated with 3-aminotriazole (3AT), which served as the positive control. In contrast, eIF2α phosphorylation is not increased in Ctk1-depleted cells. (B and C) Consistent with an inhibition of translation initiation by deletion of Ctk1, the polysome profiles of Δctk1 cells (C) showed an increased 80S peak with a concomitant decrease in polysomes compared to wild-type (wt) cells (B). The polysome/monosome (80S) (P/M) ratio was calculated by integrating the area under the respective peaks after subtraction of the values of the baseline. Values are means ± standard errors of the means (SEM) (error bars) from three independent experiments. Changes in the P/M ratio of Δctk1 and Ctk1-depleted cells compared to wt cells are statistically significant (P < 0.05 by Student's t test). (D) 48S formation is impaired in Δctk1 cells, providing further evidence that translation is shut down nonspecifically in this strain. In contrast to the defect observed for Ctk1-depleted cells (Fig. 5F), translation initiation is affected at the stage of 48S complex formation when cells are stressed (30, 32). The incorporation of RPL38 mRNA into 48S initiation complexes analyzed by an initiation assay is increased in Ctk1-depleted extracts (Fig. 5F) and stays the same in Δctk1 extracts (D). Since 80S complex formation is also decreased in Δctk1 extracts, a decrease in 48S complex formation is probably masked. A defect in 48S complex formation is also consistent with increased mRNP formation. The nonhydrolyzable GTP analogue GMP-PNP, which prevents subunit joining and therefore leads to accumulation of 48S complexes, was added to the initiation assay for better analysis of 48S initiation complexes. The error bars represent the standard deviations from at least three independent experiments. In summary, Δctk1 cells have a defect in translation initiation most likely caused by stress that results from its severe growth impairment (see the text).