FIG 3.
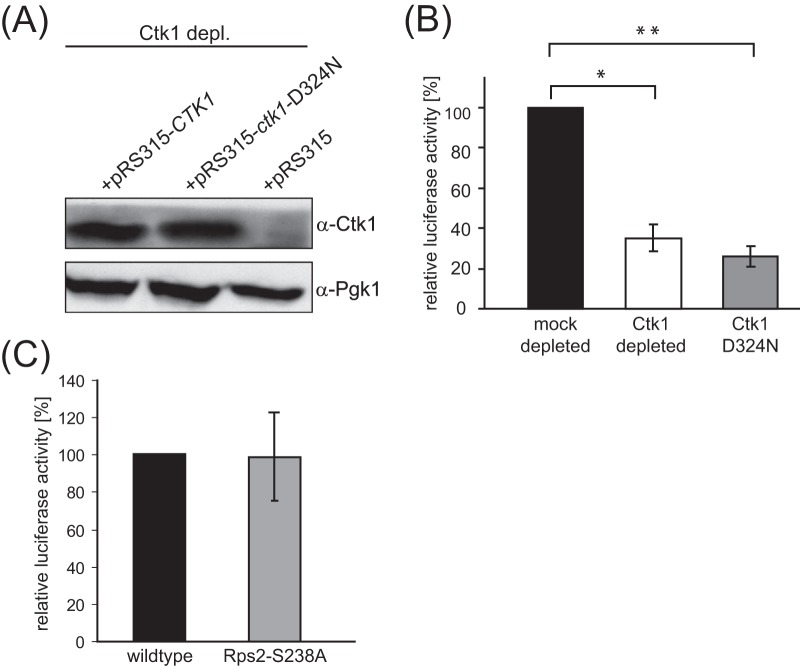
Ctk1's kinase activity is required for its function in translation. Translation active extracts were prepared from cells expressing CTK1 from the GAL1 promoter and containing a plasmid encoding either wt Ctk1, the kinase dead Ctk1 mutant Ctk1-D324N (24), or an empty plasmid. After the cells were shifted to glucose-containing medium, only the CTK1 copy on the plasmid was expressed. (A) Cellular levels of the Ctk1 wt protein and the D324N mutant are similar. Ctk1 depl., Ctk1 depletion; α-Ctk1, anti-Ctk1 antibody. (B) Translation of a luciferase reporter mRNA is reduced to 30% in Ctk1-depleted extracts as well as in extracts expressing Ctk1-D324N after Ctk1 depletion. The values for mock- and Ctk1-depleted and mock-depleted and Ctk1-D324N cells are significantly different (*, P < 0.05, and **, P < 0.01, by Student's t test). (C) The missing phosphorylation of Rps2 on S238 in Ctk1-depleted cells is not responsible for the strong translation defect in Ctk1-depleted cells. In contrast to translation fidelity (16), the overall translation rate of extracts of cells expressing a wild-type Rps2 or Rps2-S238A is the same as that measured by a luciferase reporter assay.