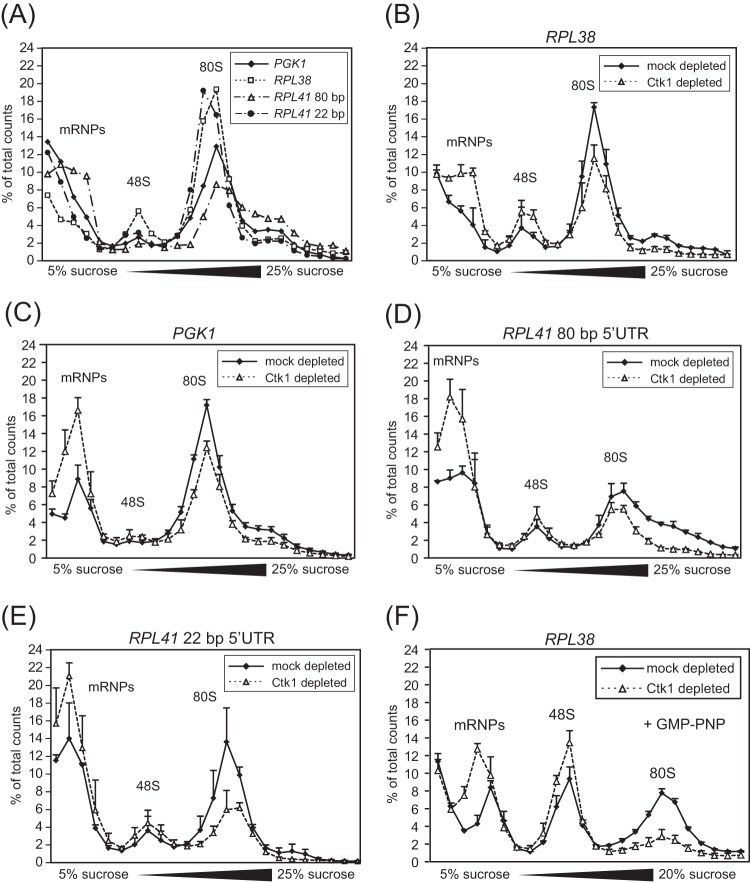
FIG 5.
In extracts of Ctk1-depleted cells, formation of 80S initiation complexes is decreased. (A) Incorporation of PGK1, RPL38, RPL41 with 80-bp 5′UTR (RPL41 80 bp), and RPL41 with 22 bp 5′UTR (RPL41 22 bp) into initiation complexes was analyzed in initiation reactions of translation active extracts. The fractions containing mRNPs, 48S, and 80S complexes are indicated. (B to E) In comparison to mock-depleted cells, Ctk1 depletion caused a decrease in incorporation of RPL38 mRNA (B), PGK1 mRNA (C), RPL41 mRNA with 80-bp 5′UTR (D), and RPL41 mRNA with 22 bp 5′UTR (E) into 80S initiation complexes. 80S formation was decreased to 68% ± 4% for the RPL38 mRNA, to 54% ± 16% for the RPL41 (22-bp) mRNA, to 68% ± 8% for the RPL41 (80-bp) mRNA and to 70% ± 4% for the PGK1 mRNA. Free mRNPs and, to a lesser extent, mRNAs bound to 48S initiation complexes are increased upon Ctk1 depletion with all mRNAs tested. Differences in the 80S peak area between Ctk1- and mock-depleted cells are statistically significant (P < 0.05 by Student's t test). (F) The incorporation of RPL38 mRNA into 48S initiation complexes is increased in Ctk1-depleted extracts. The experiment was performed as described above for panels A to E except for the addition of the nonhydrolyzable GTP analogue GMP-PNP, which prevents subunit joining and therefore leads to accumulation of 48S complexes. Differences in the 48S peak area between Ctk1- and mock-depleted cells are statistically significant (P < 0.05 by Student's t test). Each error bar represents the standard deviation of each fraction from at least three independent experiments.