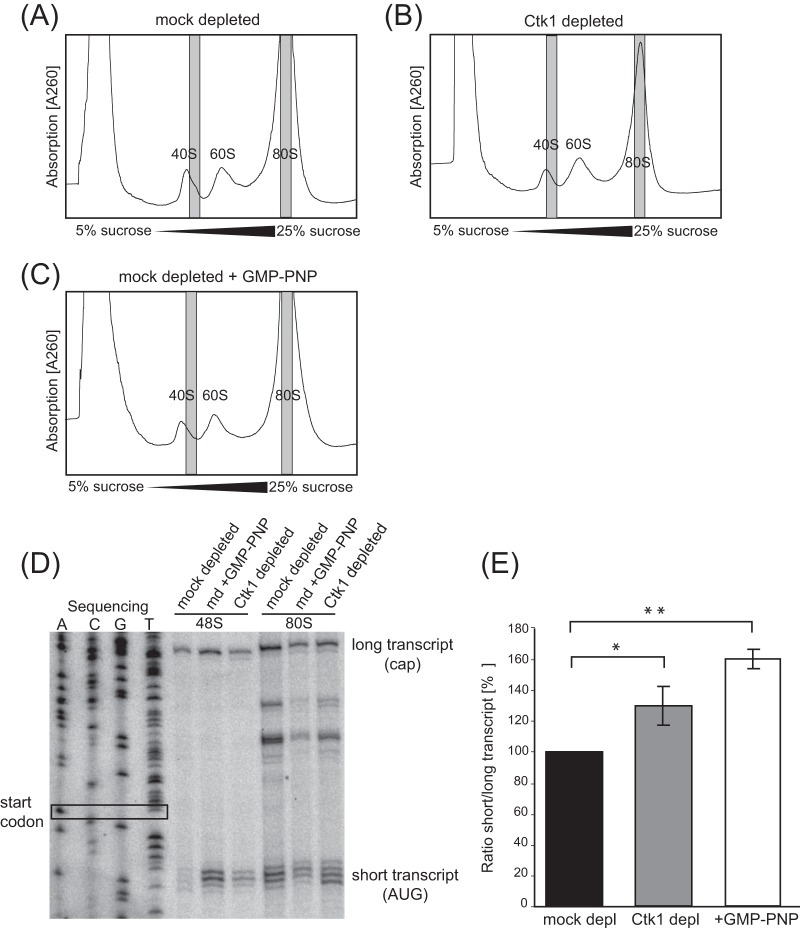
FIG 6.
Loss of Ctk1 function causes 40S subunits to accumulate at the start codon of the RPL38 mRNA in vitro. (A to C) Gradient fractions (in gray) of 48S and 80S initiation complexes were taken from mock-depleted (A), Ctk1-depleted (B), and GMP-PNP-treated mock-depleted extracts (C). (D) The 40S subunit accumulates at the start codon of 48S initiation complexes in Ctk1-depleted extracts. Toeprints of fractions taken from panels A to C were determined by primer extension and analysis on a sequencing gel. The short toeprint is produced when the 40S subunit is located at the start codon (AUG), whereas the long transcript is generated when the primer is extended to the cap of the mRNA. The plasmid DNA of the template for the mRNA used was sequenced to determine the position on the gel. (E) Quantification of the ratios of the short transcript versus the long transcript of the 48S initiation complexes shown in panel D. The signal for the short transcript is significantly increased in Ctk1-depleted extracts in comparison to mock-depleted extracts. The error bars represent the standard deviations from three independent experiments. The values for mock- and Ctk1-depleted and mock-depleted and GMP-PNP-treated cells are significantly different (*, P < 0.05, and **, P < 0.01, by Student's t test).