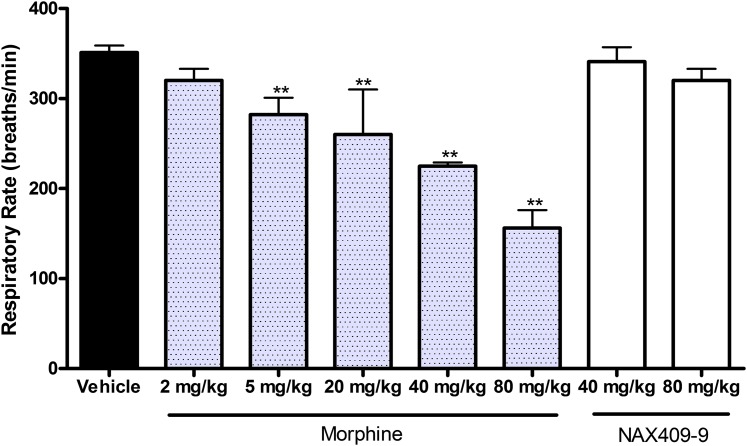
Fig. 8.
Effects of NAX 409-9 and morphine on respiratory rate in mice. Following compound (morphine, 2, 5, 20, 40, 80 mg/kg; NAX 409-9, 40, 80 mg/kg) or vehicle administration, mice were placed under light restraint and respiratory rate was determined using a pressure transducer placed adjacent to the abdominal wall. Respiratory rates were compared with the group mean for vehicle-treated mice (N = 19). Morphine at doses >5 mg/kg decreased respiratory rate (**P < 0.01), in comparison with vehicle, whereas NAX 409-9 did not decrease respiratory rate. Group sizes for morphine and NAX 409-9 were N = 4–8.