Figure 1. High levels of SCF correlates with poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma.
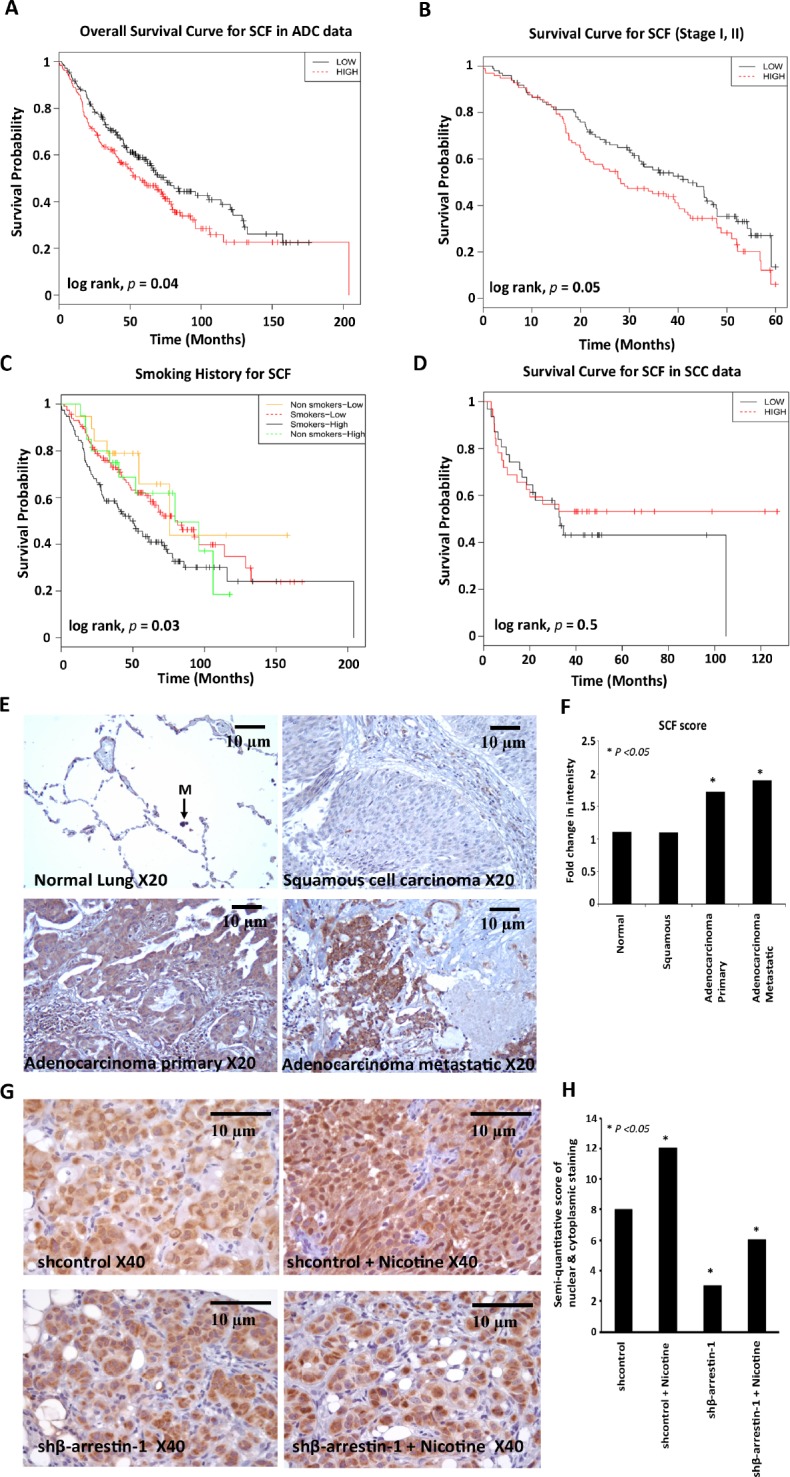
(A) Overall survival curve for SCF in 360 lung adenocarcinoma samples from the NCI Directors Challenge Set (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curve for SCF in stage I, II patients from the NCI Directors Challenge Set, (C) Overall survival curve for SCF according to smoking history in the NCI Directors Challenge Set (p value is significant between smokers with low and high SCF expression) (D) Recurrence free survival curve for SCF in squamous cell carcinoma data (n = 75) from the SKKU (Sungkyunkwan University) dataset. (E) IHC staining of SCF in Human Lung Cancer TMA using anti-human SCF antibody; representative images of SCF expression in normal lung tissue (M, Macrophage), squamous cell carcinomas, adenocarcinomas and metastatic carcinomas are shown. Magnification 20X, scale bar = 10μm. (F) Quantification of SCF immunostaining. (G) IHC staining of SCF from mice lung tumor sections revealed that SCF expression was significantly higher in tumors from nicotine treated mice (shcontrol nicotine) compared to tumors from vehicle treated mice implanted with shcontrol cells. SCF expression was significantly reduced in the β-arrestin-1 depleted cells (shβ-arrestin-1 and shβ-arrestin-1 nicotine) as compared to Shcontrol cells. Magnification 40X, scale bar = 10μm (H) Quantification of SCF immunostaining.
