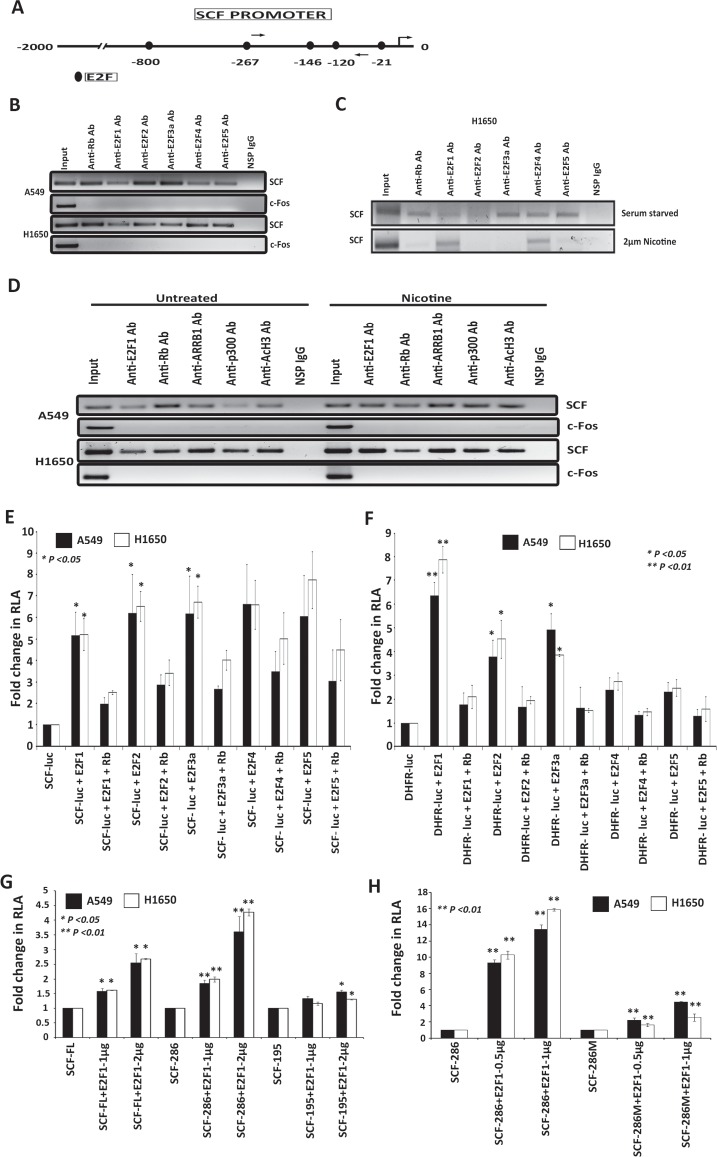
Figure 3. E2Fs regulate the expression of SCF in lung cancer cells.
(A) Schematic of SCF promoter showing putative E2F binding sites; arrows indicate the location of ChIP assay primers. (B) ChIP assays conducted on SCF promoter using the E2Fs antibodies. c-Fos promoter was used as a negative control for E2F1 binding and a non-specific IgG was used as a negative control for IP. (C) ChIP assays showing the occupancy of E2F1 and E2F4 on the SCF promoter in H1650 cells upon nicotine stimulation. (D) ChIP assays showing the occupancy of E2F1 and ARRB1 on the SCF promoter in A549 and H1650 cells upon nicotine stimulation. (E) Transient transfection experiments in A549 and H1650 cells shows that E2Fs could induce SCF promoter and E2F1 to 3 repressed by full length Rb, (F) Transient transfection experiments showing that DHFR is induced by E2F1 to 3 acted as a positive control. (G) Transient transfection results show that SCF-FL and SCF-286bp promoter fragment was E2F1 response while the shortest fragment 195bp that did not have E2F binding sites was not E2F1 responsive. (H) An E2F site mutant of the shortest SCF promoter fragment (SCF286M) showing significantly lower response to E2F1 in co-transfection assays.