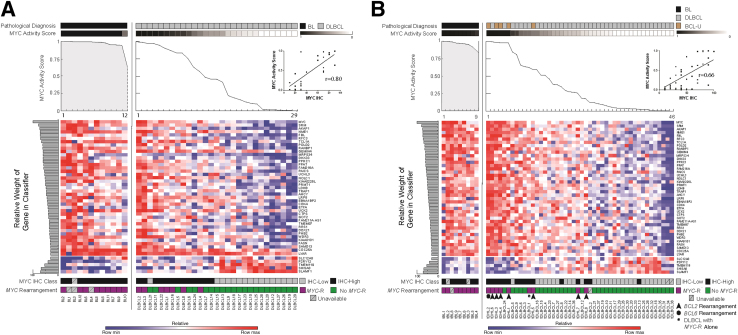
Figure 5.
A: Leave-one-out cross-validation of the final profiling panel and MYC activity classifier for the training cohort. Burkitt lymphoma (BL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are segregated by pathological diagnosis, MYC activity score (line graph), the relative expression of the indicated transcripts (heat map), including the relative contribution of each to the classifier (horizontal, shaded bar graphs), MYC IHC class (MYC IHC-Low ≤50%, IHC-High >50), and MYC rearrangement status. Inset: The correlation between MYC IHC and MYC activity score for DLBCL only (Spearman r = 0.80; 95% CI, 0.6–0.9). B: Results of the final profiling panel and MYC activity classifier for the test cohort, BL, DLBCL, and B-cell lymphoma unclassifiable (BCL-U), are segregated by pathological diagnosis, MYC activity score (line graph), the relative expression of the indicated transcripts (heat map), including the relative contribution of each to the classifier (horizontal, shaded bar graphs), MYC IHC class (MYC IHC-Low ≤50%, IHC-High >50%), and MYC rearrangement status. Genetic double hit lymphomas are numbered and additional gene rearrangements are indicated by arrowheads (BCL2-) or a circle (BCL6-). The single-hit DLBCL, with MYC-rearrangement only, is indicated by an asterisk. Inset: The correlation between MYC IHC and MYC activity score for non-BL only (Spearman r = 0.66; 95% CI, 0.44–0.8). Max, maximum; min, minimum.