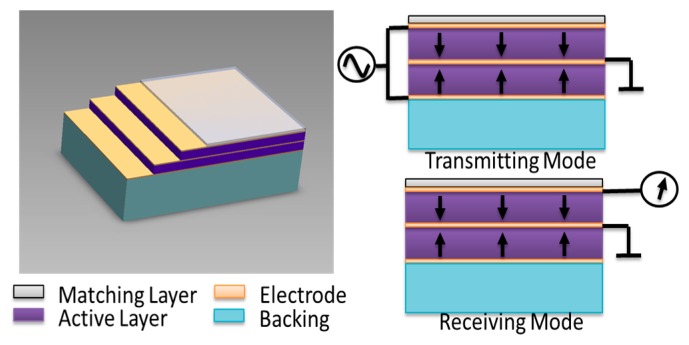
Figure 4.
Schematic view of a dual-layer, dual-frequency transducer (left) and its operation for transmitting and receiving (right). When transmitting, both active layers are electrically connected in parallel and are excited by the same signal, effectively behaving as a single, active element at f0. When receiving, the front layer records the majority of the signal with a resonance at twice the transmission frequency (2f0) because the thickness of the active layer has effectively been halved. Figure reprinted with permission from [71].