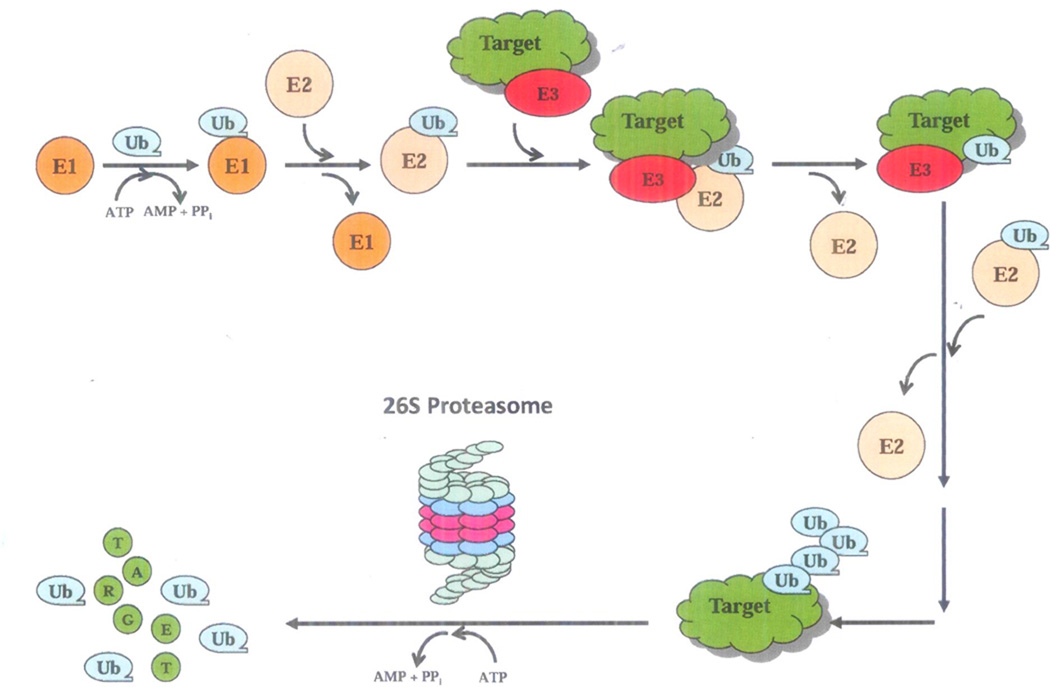
Fig. 1. The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS).
The UPS-mediated protein degradation is an ATP-dependent process, involving two distinct steps, ubiquitination and degradation. First, ubiquitin (Ub) is covalently linked to a target protein by a multi-enzymatic system consisting of Ub-activating (E1), Ub-conjugating (E2), and Ub-ligating (E3). E1 activates an Ub monomer and transfers it to E2. E3 facilitates E2 to transfer the Ub to a reactive lysine residue of the target protein. The polyubiquitinated protein is then recognized by the 19S regulatory complex of the 26S proteasome and fed into the 20S catalytic core for degradation into oligopeptides and the ubiquitin molecules recycled.