Table 1. Electronic effect of R′ substituents on the relationship between the structure and photophysical properties of Seoul‐Fluors.[a]
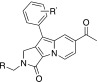 .
.
| Compound | R′ | σp[b] | Eh[c] | λabs[d] | λem[e] | ΦF[f] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 4‐NEt2 | −0.72 | −0.160 | 441 | – | 0.00 |
| 11 | 4‐NH2 | −0.66 | −0.169 | 419 | 546 | 0.03 |
| 12 | 4‐OH | −0.37 | −0.200 | 413 | 572 | 0.12 |
| 13 | 4‐OMe | −0.27 | −0.195 | 412 | 555 | 0.20 |
| 14 | 4‐Me | −0.17 | −0.215 | 404 | 534 | 0.38 |
| 15 | 4‐H | 0 | −0.227 | 403 | 523 | 0.50 |
| 16 | 4‐F | 0.06 | −0.225 | 402 | 525 | 0.47 |
| 17 | 4‐CF3 | 0.54 | −0.249 | 405 | 514 | 0.64 |
| 18 | 4‐CN | 0.66 | −0.247 | 398 | 512 | 0.63 |
| 19 | 3,4‐(CN)2 | – | −0.262 | 402 | 500 | 0.72 |
[a] Measurements were made in methanol. [b] σp is the Hammett constant of the R′ substituent at the para position.9 [c] Calculated energy in hartree of the HOMO level of the phenyl moiety. [d] Longest absorption wavelength maximum. [e] The emission wavelength for excitation at the longest absorption wavelength maximum. [f] Absolute fluorescence quantum yield.
