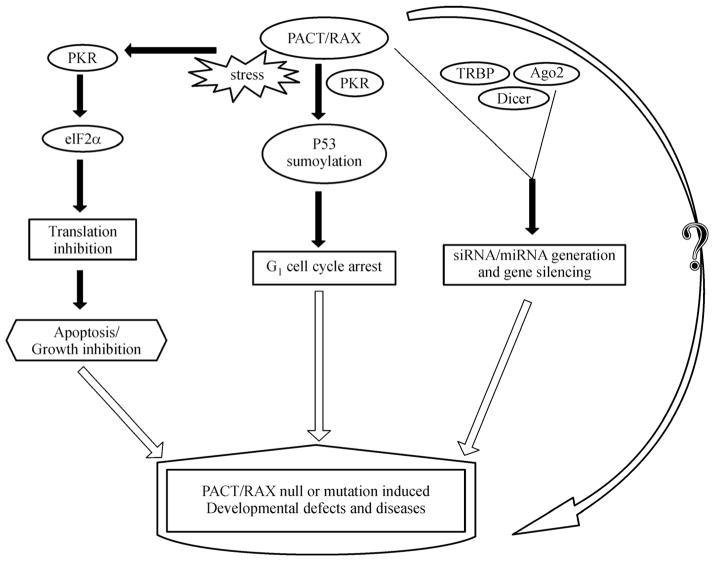
Figure 1.
Role of PACT/RAX in the development and diseases. PACT/RAX is activated by various cellular stresses and interacts with PKR, resulting in eIF2α phosphorylation and subsequent inhibition of protein synthesis and induction of apoptosis or growth inhibition. RAX/PACT-PKR interaction promotes p53 sumoylation, leading to G1 cell cycle arrest. PACT/RAX associates with TRBP, Dicer and Ago2 and regulates siRNA/miRNA generation and gene silencing. PACT/RAX knockout or mutation leads to diseases and serious development defects through unknown mechanisms. PACT/RAX is an important stress responsive protein and plays important in cell physiology and development.