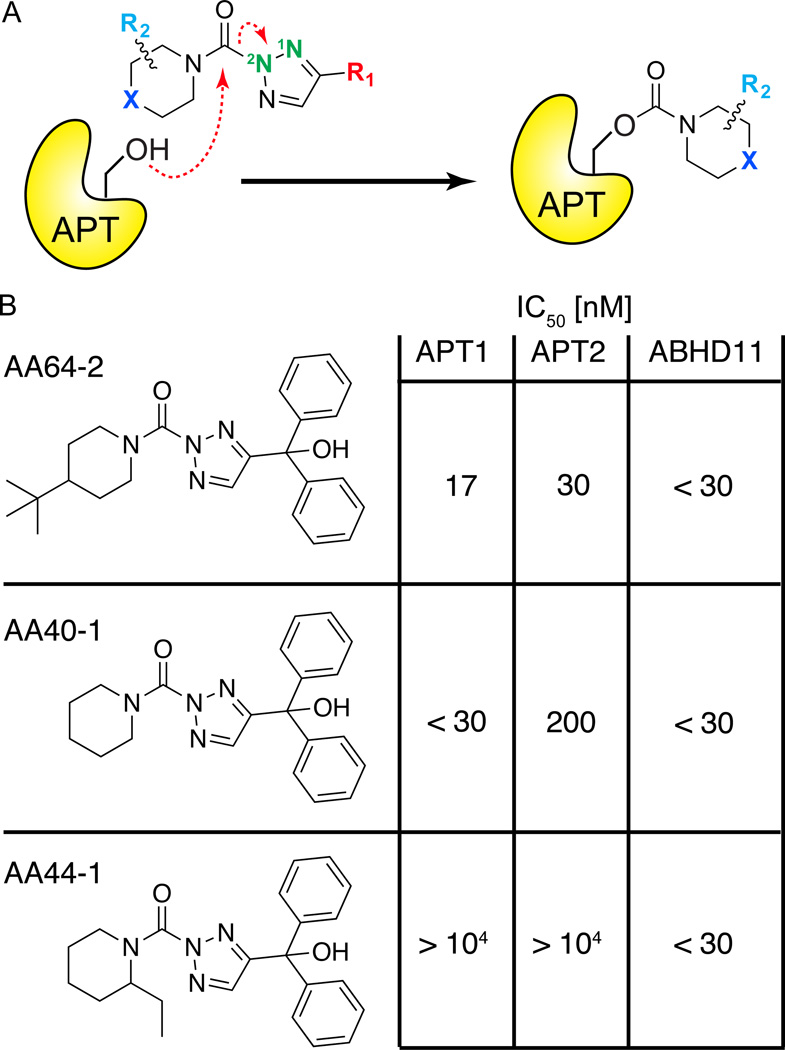
Figure 6. Triazole urea covalent APT inhibitors.
(A) Mechanism of triazole urea inactivation of APT enzymes. The APT nucleophilic serine hydroxyl attacks the urea, releasing the triazole and leaving a stable carbamate adduct, inactivating the enzyme. (B) Selectivity and potency of optimized triazole urea inhibitors determined by gel-based competitive ABPP. AA64-2 is highly potent and selective for APT enzymes, with the exception of the uncharacterized hydrolase ABHD11. AA44-1 is highly selective for ABHD11, and can be used as a control probe.