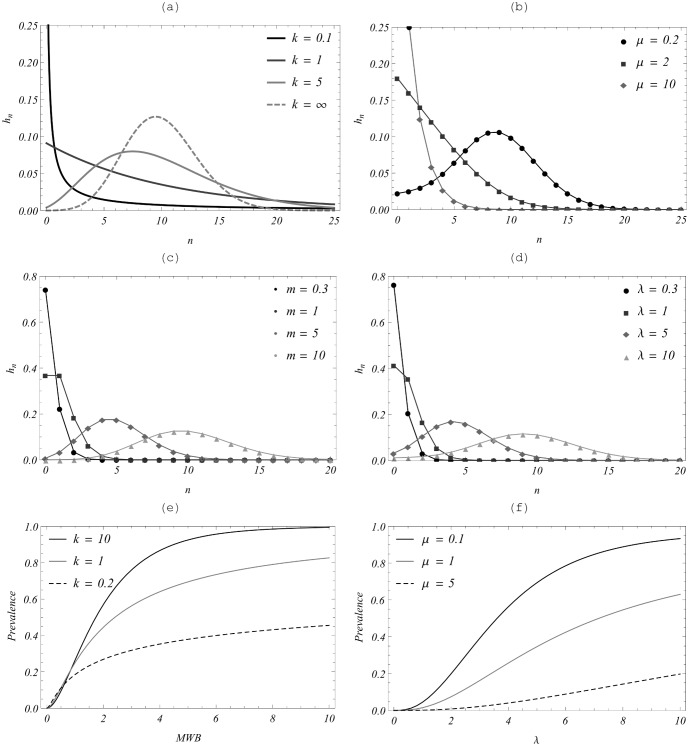
Figure 2. Comparison of worm distribution patterns for a negative binomial-based MWB system vs. a SWB system.
Here, all SWB distributions (right-hand panels) are produced from an uninfected source  . (a) NB-MWB with fixed mean
. (a) NB-MWB with fixed mean  and increasing k (
and increasing k ( is the limiting Poisson case); (b) Equilibrium SWB distribution for uninfected source with FOI (mean)
is the limiting Poisson case); (b) Equilibrium SWB distribution for uninfected source with FOI (mean) 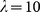 , and varying demographic parameter
, and varying demographic parameter 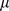 (see equation (13));
(see equation (13)); 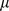 plays the role of aggregation k for NB, with small
plays the role of aggregation k for NB, with small 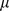 corresponding to large (infinite) k. Panels (c−d) Poisson distributions with different means,
corresponding to large (infinite) k. Panels (c−d) Poisson distributions with different means, 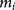 (left panel) vs. SWB distributions with different
(left panel) vs. SWB distributions with different 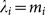 (right panel) exhibit striking similarity. Panels (e)−(f) compare infectious prevalence
(right panel) exhibit striking similarity. Panels (e)−(f) compare infectious prevalence  for the two models as a function of NB-MWB w or SWB
for the two models as a function of NB-MWB w or SWB 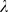 .
.