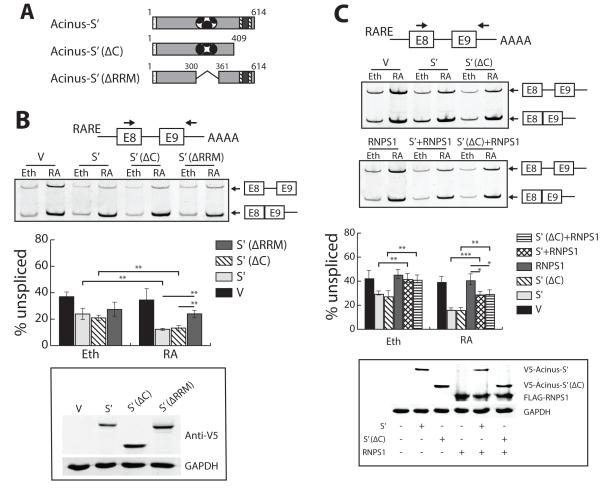
Figure 4. The synergistic effect of RA and Acinus on the splicing of a RA-responsive reporter minigene containing a weak 5′ splice site requires the RRM domain of Acinus, and is independent of RNPS1.
A. Schematic diagram of wild type and Acinus-S’ mutants. B. The RRM domain is critical for the RA-dependent activity of Acinus in the splicing of RARE-tubg1E8-E9 pre-mRNA. C. Only the RA-independent effect of Acinus on the splicing of RARE-tubg1E8-E9 pre-mRNA is repressed by RNPS1. In Panels B and C, 293A cells were transfected with RARE-tubg1E8-E9 splicing reporter DNA, RARβ expression vector DNA, and one of the following V5-tagged expression vector DNAs [wild type V5-Acinus-S’, V5-Acinus-S’ (ΔC), V5-Acinus-S’ (δRRM) or V5-empty expression vector DNA (see schematic diagram in Panel A)], and 3XFlag-tagged RNPS1 expression vector DNA (Panel C only). Twenty-four hrs after transfection cell were treated with ethanol or 10−6 M RA for an additional 24 hr. Total RNA was prepared and used to analyze splicing as described in the legend to Figure 1 and whole cell protein extracts were analyzed by Western blot using V-5 antibody to detect wild type and mutant Acinus-S’, Flag antibody to detect RNPS1 and GAPDH antibody (C). Values represent mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. V, V5 empty vector; S’, V5-Acinus-S’; S’(δC), V5-Acinus-S’ (ΔC); S’(ΔRRM), V-Acinus-S’ (ΔRRM); Eth, ethanol; RA, retinoic acid. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, unpaired t test.