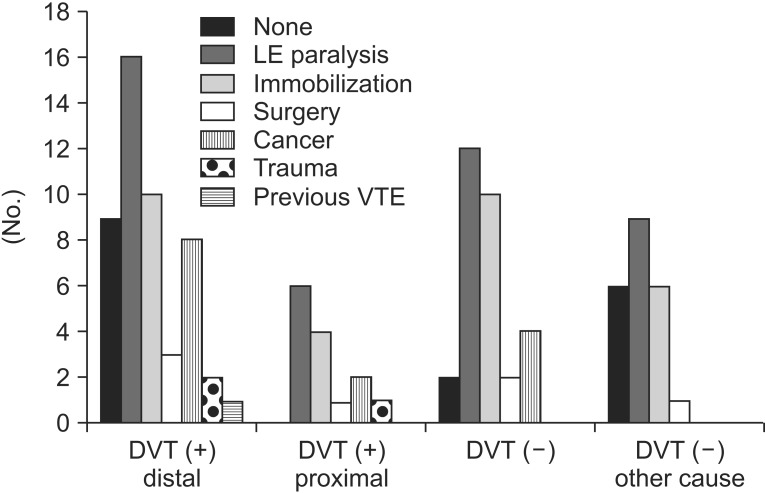
Fig. 3.
The graph shows distributions of risk factors of VTE among four groups: DVT (+) distal, DVT distal to inguinal ligament; DVT (+) proximal, DVT proximal to inguinal ligament (in abdomen/pelvis) or with compression of other structures; DVT (-), no DVT detected; and DVT (-) other causes, no DVT and other causes of leg swelling detected). The relative proportion of LE paralysis in DVT (-) and DVT (-) with other cause groups was higher, similar to DVT (+) group. Therefore in the patients with LE paralysis usually present in the department of rehabilitation there are various causes of leg swelling and some causes can be found more easily by computed tomography venography than other study. DTV, deep vein thrombosis; VTE, venous thromboembolism; LE, lower extremity.