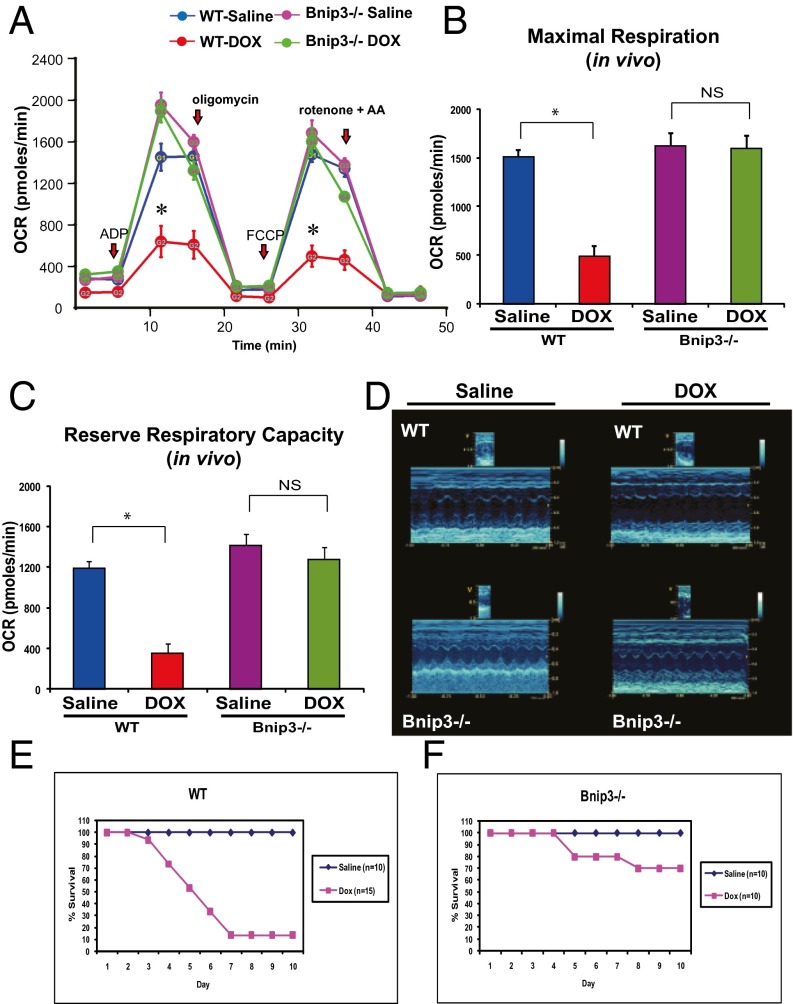
Fig. 9.
Bnip3−/− mice are resistant to DOX-induced mitochondrial respiratory chain defects and cardiac dysfunction. (A) Respiratory rates of heart mitochondria isolated from surviving WT mice and Bnip3 −/− mice treated with vehicle or DOX after 10 d of treatment. OCR was measured with a Seahorse metabolic analyzer; details are provided in Fig. 4. Saline-treated WT mice are shown in blue; DOX-treated WT mice, in red; saline-treated Bnip3−/− mice, in pink; DOX-treated Bnip3−/− mice, in green. (B and C) Histograms showing relative MMR and RRC from data shown in A. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. OCR (pmol/min) from 20 μg of isolated heart mitochondria from each condition tested, n = 5 replicates; P < 0.05. *Statistically different from vehicle-treated control. NS, statistically nonsignificant. (D, Upper) Representative M-mode echocardiography images of saline- and DOX-treated WT and Bnip3−/− mice at 5 d posttreatment. (Lower) M-mode images of Bnip3−/− mice from saline- and DOX-treated age-matched littermates. (E and F) Survival curves for vehicle- and DOX-treated WT (E) and Bnip3−/− (F) mice.