Figure 6.
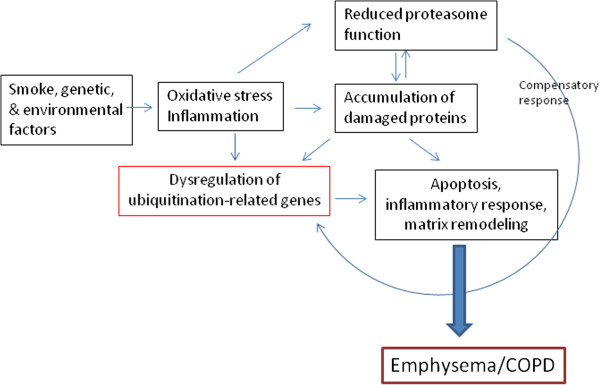
Proposed model of dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system leading to the pathogenesis and progression of emphysema/COPD. Oxidative stress and inflammation induced by smoke, genetic or environmental insults result in dysregulation of ubiquitination-related genes and impairment of the proteasome function. Accumulation of abnormal proteins in the lung as a result of increased production and decreased degradation causes further damage of the proteasome function and dysregulation of UPS-related genes. Aberrant regulation of the UPS results in apoptosis, inflammation, and matrix remodeling, pathogenic characteristics of emphysema/COPD. Damaged proteasome function can also cause compensatory upregulation of genes associated with the UPS.
