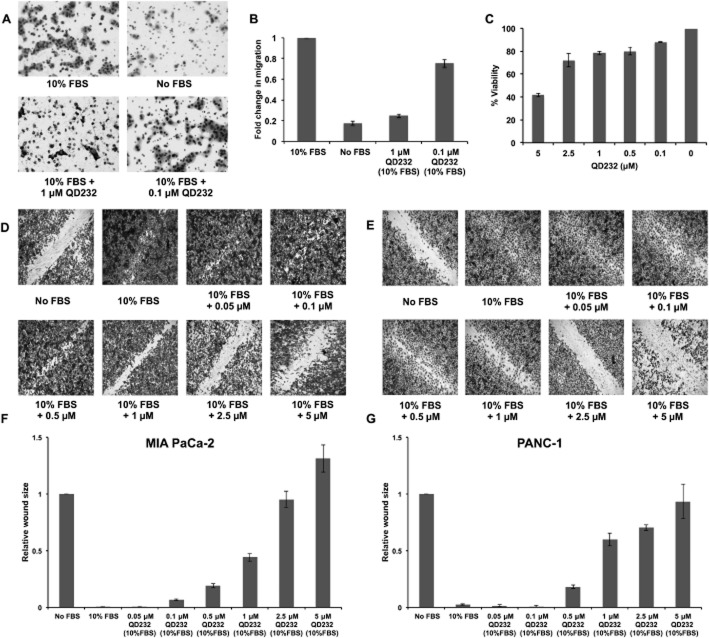
Figure 3.
QD232 inhibits cell migration. (A) A 24 h treatment with QD232 (1 μM) resulted in decreased migration of serum-starved MIA PaCa-2 cells through the membrane of a Boyden chamber in the presence of 10% FBS stimulation. Cells were imaged after fixing with methanol and staining with Giemsa using a Nikon microscope with 10× objective. (B) Quantification of data (means ± SD) shown in (A); effect induced by both concentrations of QD232 were significantly different from control (10% FBS only); P < 0.05. (C) Cell viability (means ± SD) as determined by MTT assay of MIA PaCa-2 cells treated with QD232 concentrations that were used in the cell migration assays under identical conditions. (D, E) Treatment with QD232 for 24 h inhibited closure of wounds stimulated by 10% FBS in serum-starved MIA PaCa-2 (D) and PANC-1 (E) cells in a dose-dependent manner. Media without FBS was used as a control for the inhibition of wound closure. Cells were imaged after fixing with methanol and staining with Giemsa using BD Pathway 435 High-Content Bioimager with a 4× objective. Representative images of three independent experiments are shown. (F, G). Quantification of images (means ± SD) shown in D and E respectively. Images were quantified using ImageJ software (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/). All concentrations of QD232, except the lowest (0.05μM in F, and 0.05 and 0.1 μM in G), had significant effects, compared with 10% FBS only; P < 0.05.