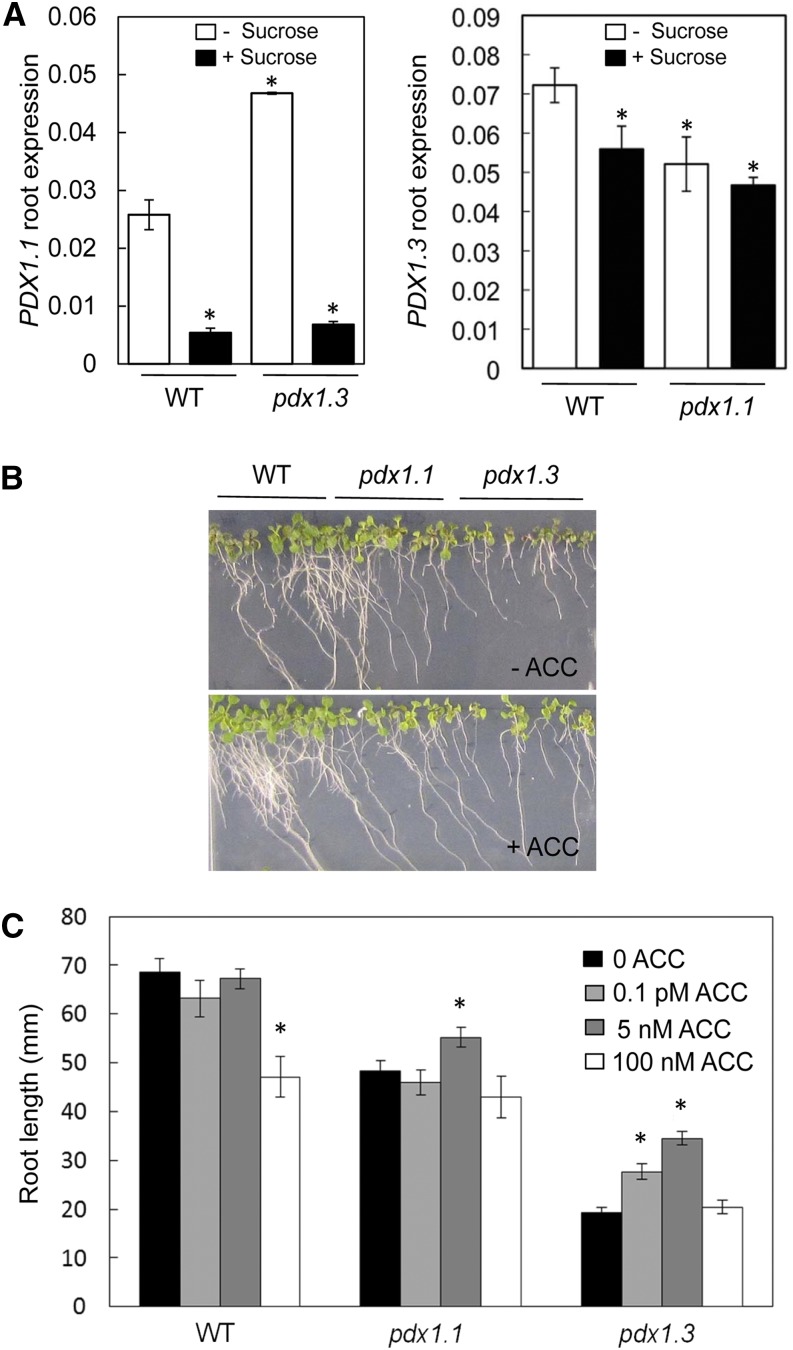
Figure 5.
Exogenous Suc represses PDX1.1 expression, but application of ACC can partially rescue the pdx1 root phenotype. A, Expression of PDX1.1 (left) and PDX1.3 (right) in roots of wild-type (WT) Col-0 and pdx1.3 or pdx1.1 in the absence or presence of 1% (w/v) Suc. Seedlings were allowed to grow until 10 DAG. The data are from at least three biological repetitions. Error bars represent se. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) when treatments are compared with the wild type grown in the absence of Suc. B, Growth of the wild type, pdx1.1, and pdx1.3 in the presence of 1% (w/v) Suc as well as in the absence (top) or presence (bottom) of 5 nm ACC. The experiment was done three times, yielding similar results; images were captured at 10 DAG. C, Root length of wild-type, pdx1.1, and pdx1.3 seedlings at 10 DAG grown on 1% (w/v) Suc in the presence or absence of ACC (0–100 nm as indicated). The data are averages of three biological replicates; measurements were performed using ImageJ software (http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/). Error bars represent se. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) when compared with the wild type in the absence of ACC.