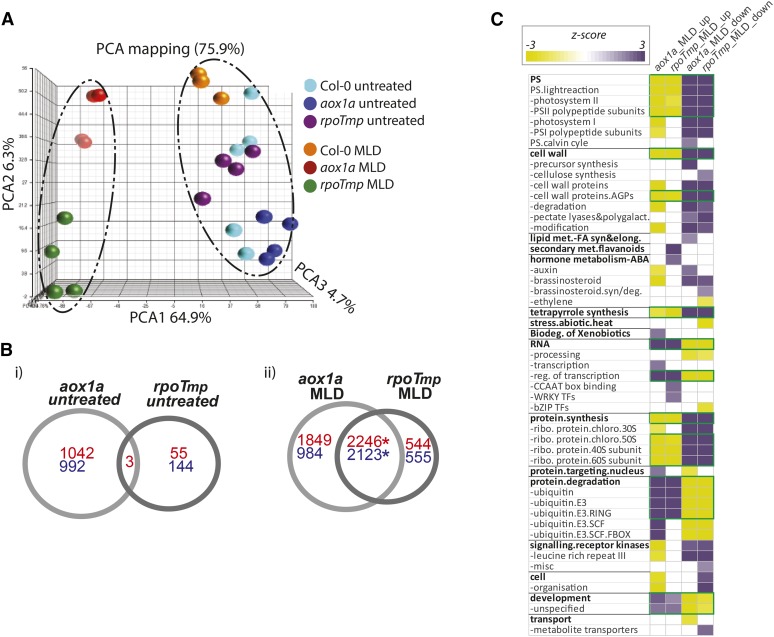
Figure 2.
Transcriptomic responses to MLD environmental stress in rpoTmp and aox1a plants show common, dramatic, and widespread changes in transcription. A, Three-way principle component analysis (PCA) was carried out for all microarray gene chips, showing a clear separation on PCA1 (64.9%) for aox1a and rpoTmp under MLD conditions. B, Venn diagrams showing the overlap for significantly differentially expressed transcript responses for aox1a and rpoTmp plants compared with wild-type (Col-0) plants (i) and after MLD treatment compared with respective untreated mutant plants (ii). Up-regulated transcripts are shown in red, whereas down-regulated transcripts are shown in blue. *, Significant overlap according to a χ2 test for significance (P < 0.0001). C, Functional categorization analysis (using Pageman) for transcripts changing in abundance in response to stress for both aox1a and rpoTmp plants. Over- and underrepresented categories are shown in purple and yellow, respectively. Boxed in green are the functional categories that are overrepresented in gene sets and show a common response under MLD stress. FA, Fatty acid; syn/deg, synthesis/degradation; bZIP, basic leucine zipper transcription factor; ribo, ribosome; chloro, chloroplast.