FIGURE 3.
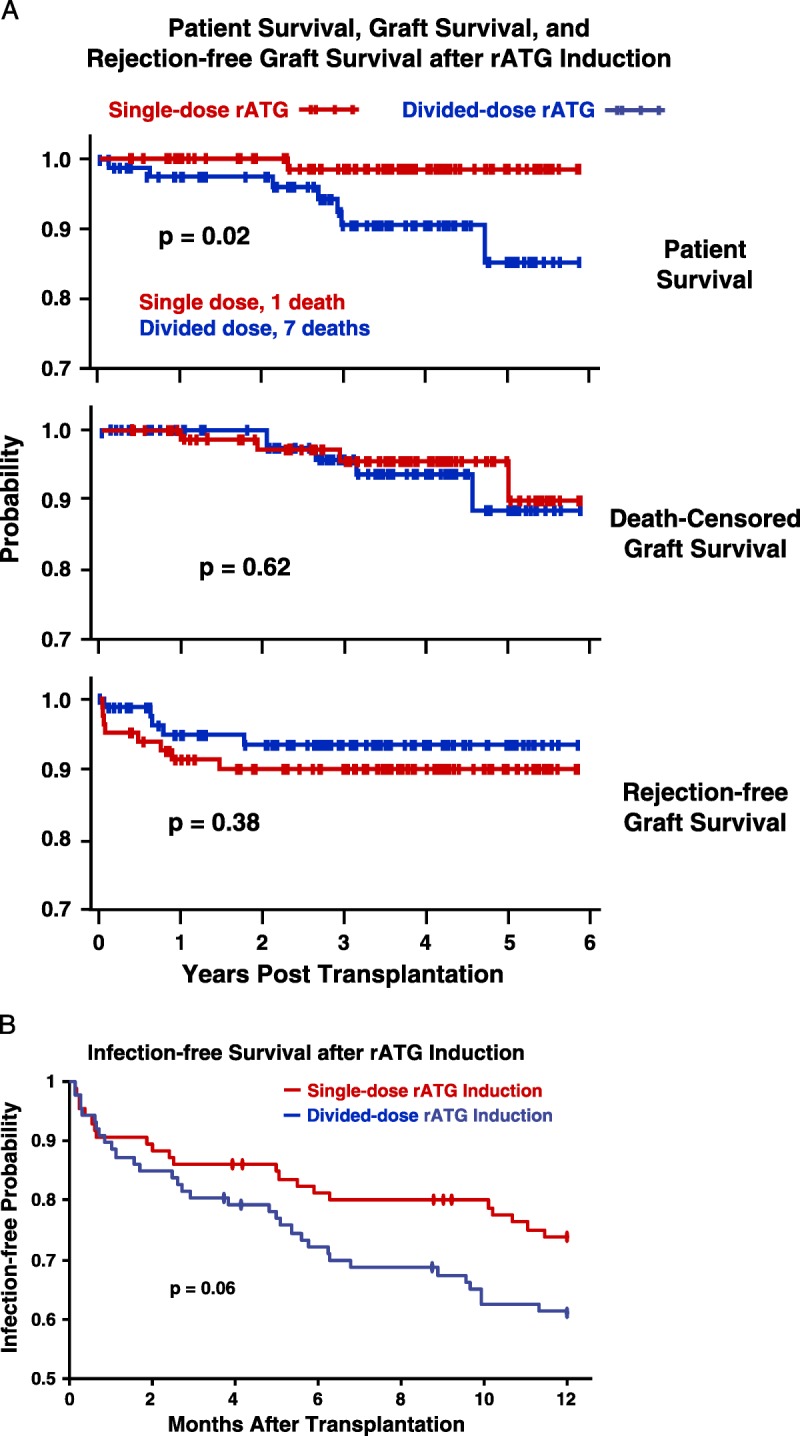
A, Rates of patient survival, graft survival, and rejection were compared with Kaplan-Meier analyses and log-rank tests. Patient deaths occurred at an average of 2.3±1.4 years after transplantation, of causes that included myocardial infarction, cancer, sepsis, drug overdose, and pulmonary embolus (Table S2, SDC, http://links.lww.com/TP/B12). Rejection was confirmed by ultrasound-guided biopsies (biopsy-proven acute rejection) graded according to Banff 1997 or 2005 criteria.73. There were eight acute cellular rejection episodes in the single-dose group; five Banff grade IA, three grade IB. There were five cellular rejections in the divided-dose group; 1 grade IA, 3 grade IB, 1 grade IIA. B, There were eight episodes of suspicious or borderline rejection in each group not included. There were three instances of DSA+ AMR observed among our study patients, all in the divided-dose rATGgroup, at 9 days, 9months, and 14 months after transplantation. Only one of these grafts has been lost, at 2 years in the patient who experienced AMR at 14 months. The treatment of acute cellular rejection was guided by specific Banff classification (Table S4, SDC, http://links.lww.com/TP/B12). (B) Kaplan-Meier estimates of likelihood of infection after rATG induction and renal transplantation. The first of any infection after transplantation was scored, including pneumonia, abscess, UTI, bacteremia, “other” bacterial, BK (viruria or disease),CMV, Epstein-Barr virus, post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder, “other” viral, and fungal. C, In both rATG induction groups, lymphocyte counts immediately declined steeply after rATG infusion, but recovered significantly more rapidly in the single-dose group. D and E, T-cell subset data were obtained from only the first 80 patients because of the cost. Although CD8 numbers recovered rapidly and equally in both groups, CD4 counts and the CD4-to-CD8 ratio recovered significantly faster in the single-dose group. DSA+, donor-specific antibody positive; AMR, antibody-mediated rejection; rATG, rabbit antithymocyte globulin; CMV, cytomegalovirus; UTI, urinary tract infection.
