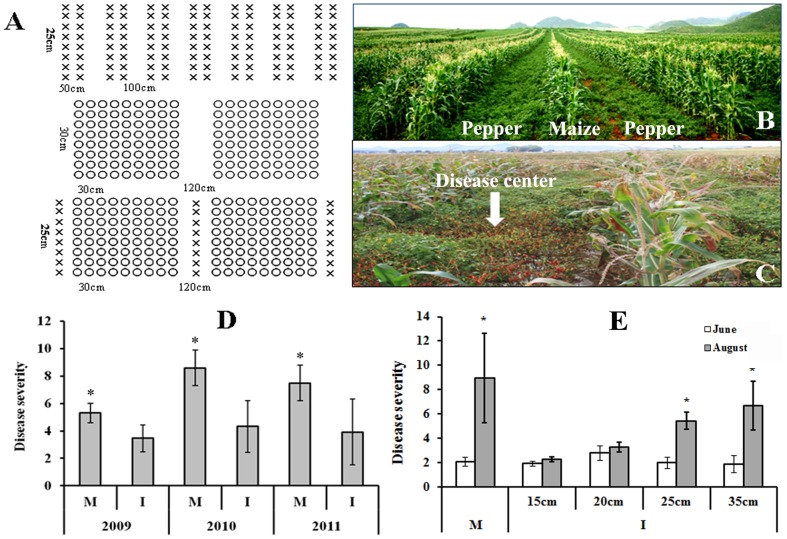
Figure 1. Maize and pepper intercropping in field and the effect on the development of pepper Phytophthora blight.
(A) Maize and pepper intercropping and monoculture patterns. Each symbol represents a plant of a different crop species: maize (×), pepper (○). In maize monoculture system, the wide inter-row spacing was 100 cm and the narrow inter-row spacing was 50 cm. The intra-row spacing was 25 cm; In pepper monoculture system, the inter-row and intra-row spacing were 30 cm×30 cm in each strip. The space between strips was 120 cm. In maize and pepper intercropping system, the width of each strip was 3.4 m, and one row of maize intercropping with nine rows of pepper was planted in each strip. The inter-row and intra-row spacing for pepper plant was 30 cm×30 cm. The intra-row spacing of maize plant was 25 cm. The inter-row spacing between maize and pepper plants was 60 cm; (B) Maize and pepper intercropped in field; (C) Pepper Phytophthora blight in intercropping system. Arrow shows the disease center. Maize can restrict pepper Phytophthora blight across the maize line; (D) Disease severity (±SE) of pepper Phytophthora blight in monoculture and maize/pepper intercropping system from 2009 to 2011. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences of monoculture compared to intercropping (Student's t test; p<0.05; n = 10); (E) Effect of maize with different intra-row spacing on the disease severity of pepper Phytophthora blight incidence (±SE) in intercropping system in 2012. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference of severity surveyed in August and June (Student's t test; p<0.05; n = 5). M and I in figure D and E represent pepper monoculture and pepper intercropping with maize, respectively.