Figure 2. Cntnap4 mutant mice show increased dopamine, but decreased GABA signaling.
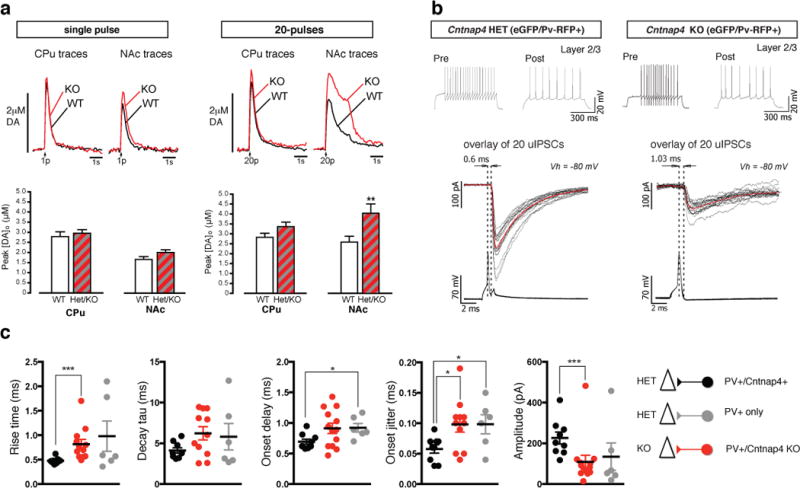
A. Evoked dopamine measurements by voltammetry in vitro in WT and mutant. Increased extracellular dopamine release in mutants vs. WT. 20 pulses lead to a significant increase in NAc. Representative traces of extracellular dopamine concentration levels [DA]o in time of WT (black) versus KO mouse (red). Distribution of peak [DA]o values for all the data points included in the analysis (n = 3 for each genotype).
B. Paired recordings between PV-positive and excitatory cells in somatosensory cortex in vitro. Examples of firing in pre- and post-synaptic cells.upon step depolarization. A single action potential evokes fast, reliable postsynaptic responses in HET. Responses smaller, slower and more unreliable in KO (in grey are the individual traces and in red the average).
C. Overall data of synaptic values for responses recorded in three groups of paired recordings. Black denotes presynaptic Cntnap4-positive PV cells in HET mice; grey denotes PV cells yet to express Cntnap4 in HET mice; red denotes PV cells in KO mice.
