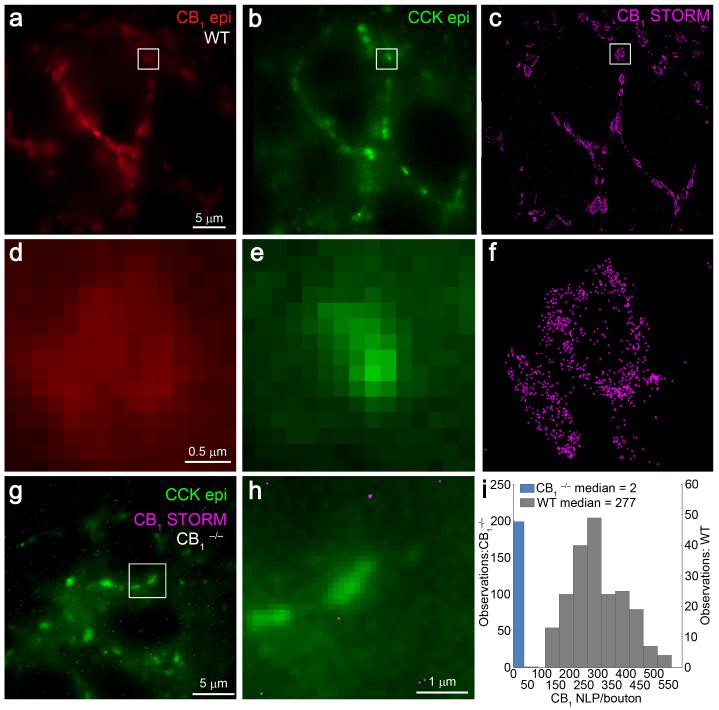
Figure 1. 3D-STORM imaging of CB1 receptors on hippocampal GABAergic axon terminals.
(a) Immunofluorescence labeling of CB1 receptors in the CA1 stratum pyramidale of CB1+/+ mice showed basket-like arrangement of CB1-positive axon terminals encircling a CB1-immunonegative pyramidal cell somata. (b) These axon terminals could also be visualized by immunofluorescence staining for the neuropeptide CCK, a neurochemical marker of CB1-expressing interneurons. (c) STORM imaging of CB1 receptors revealed identical basket-like orientation of the same perisomatic GABAergic axon terminals. (d,e) Magnifying the epifluorescence images failed to delineate the morphological structure of the respective profiles located in the boxed region or the precise nanoscale position of CB1 receptors with the axon terminals. (f) In contrast, the improved spatial resolution of 3D-STORM microscopy made it possible to reliably discern individual CB1-positive boutons located adjacently to one another, as well as to reveal localization points representing the nanoscale position of CB1 receptors. (g,h) To validate the specificity of our approach, hippocampal sections from littermate CB1−/− mice were also processed and imaged under the same conditions. In these sections, we found an almost complete absence of STORM localization points representing CB1 within CCK-immunolabeled boutons. (i) Histogram of CB1 NLP in individual CCK-positive varicosities in the CA1 stratum pyramidale of sections derived from littermate CB1+/+ (n = 3 animals; n = 208 axon terminals) or CB1−/− (n = 2 animals; n = 200 axon terminals) mice. Note that the drastically reduced CB1 NLP value in CB1−/− samples validates the specificity of the antibody, the staining process and the STORM imaging protocol.