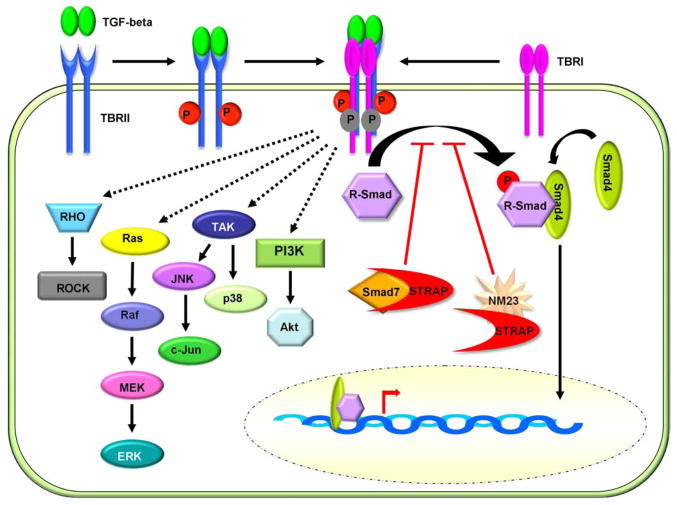
Figure 1.
The TGF-beta signaling pathways. TGF-beta signaling can be propagated through Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways. In the Smad-dependent pathway, the activated TGF-beta receptor complex phosphorylates the R-Smads, Smad-2 and Smad-3. The phosphorylated R-Smads associate with the common Smad-4 and translocate to the nucleus where they function as transcriptional activators and repressors of gene expression. The inhibitory Smad, Smad-7, inhibits activation of the R-Smads by associating with TBRI. The WD40 domain protein, STRAP, also functions as an inhibitor of Smad-dependent signaling by associating with Smad-7 and TBRI. In addition to Smad activation, The TGF beta receptor complex can induce signaling through the Ras, RhoA, TAK1, and PI3K pathways. TGF-beta mediated activation of these non-Smad pathways has been associated with cellular transformation, proliferation, EMT, and migration.