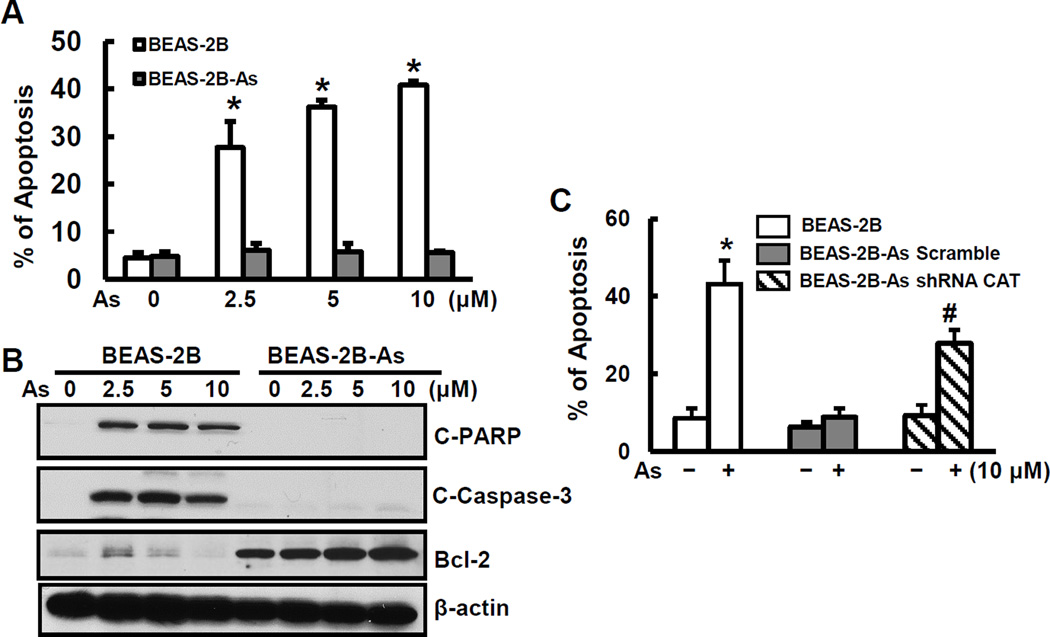
Fig. 4.
Resistance to apoptosis of arsenic-transformed cells and restoration of apoptosis by inhibition of catalase expression. (A) and (B) BEAS-2B-As and BEAS-2B cells were seeded into 6-well culture plates. Cells were treated with different concentrations of arsenic for 24 hrs. (A) The percentage of apoptotic cells was measured using flow cytometry. Data are mean±SD (n=6). * p< 0.05 compared to non-transformed cells. (B) Whole cell lysates were collected for immunoblotting analysis. Expression levels of C-PARP, C-caspase 3, and Bcl-2 were measured. (C) BEAS-2B-As were transfected with either scramble or catalase shRNA for 24 hrs. BEAS-2B, scramble arsenic-transformed (BEAS-2B-As Scramble), and shRNA catalase arsenic-transformed (BEAS-2B-As-shRNA CAT) cells were treated with 10 µM arsenic for 24 hrs followed by apoptosis analysis. Data are mean±SD (n=6). * and #, p < 0.05 compared to the BEAS-2B cells and BEAS-2B-As-shRNA CAT without arsenic treatment, respectively.