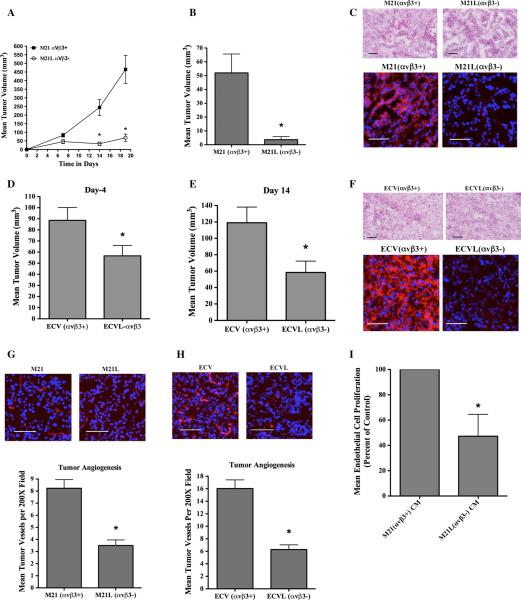
Fig. 2.
Differential impact of αvβ3 integrins on tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis in vivo. Nude mice were injected with tumor cells, and early-stage tumor growth and angiogenesis were examined. a M21 cell variants (5.0 × 106) were injected subcutaneously, and tumor growth monitored over a 19-day time course. Data bars represent mean tumor volumes ± SE from 8 to 9 mice per condition. b M21 cell variants (0.5 × 106/mouse) were injected subcutaneously, and tumor growth examined on day 7. c Representative examples of tumor tissues analyzed by H&E staining (Top) and for expression of αvβ3 (bottom) from each M21 tumor variant. Red color (bottom panels) indicates expression of αvβ3. Photographs were taken at ×200 magnification. d, e ECV cell variants (5.0 × 106/mouse) were injected subcutaneously into nude mice, and tumor growth examined on days 4 (d) and 14 (e). f Representative examples of tumor tissues analyzed by H&E staining (Top) and for expression of αvβ3 (bottom) from each ECV tumor variant. Red color (bottom panels) indicates expression of αvβ3. Photographs were taken at ×200 magnification. g, h Analysis of tumor-associated angiogenesis. Top panels Representative examples of CD31 expressing tumor vessels (Red) from each tumor variant. Photographs were taken at ×200 magnification. Bottom panels Quantification of tumor-associated CD31 expressing blood vessels. Data bars represent mean vessel counts ± SE per ×200 fields (n = 10) for each of three independent tumors from each condition. i The effects of serum-free ×10 conditioned medium (CM) from M21 or M21L cells on human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) proliferation were examined. Data bars represent mean cell proliferation following incubation with CM from each cell variant, expressed as percent of control ± SE from four independent experiments. *Indicates P values <0.05