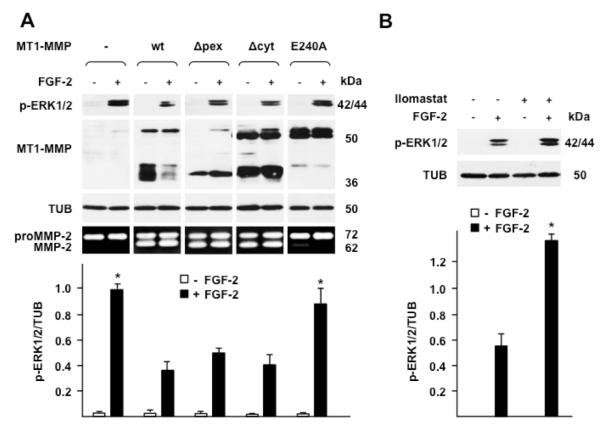
Figure 2. The proteolytic activity of MT1-MMP is required for downregulation of ERK1/2 activation by FGF-2.
Western blotting analysis of ERK1/2 activation (p-ERK1/2) and MT1-MMP expression. A. MCF-7 cells transiently transfected with wt or mutant MT1-MMP cDNAs were grown for 24 h in medium containing 0.5% FBS and treated with FGF-2 (0.75 ng/ml) for 15 min. -, empty vector; wt, wild-type MT1-MMP; Δpex, Δcyt, MT1-MMP devoid of the hemopexin or the cytoplasmic domain, respectively; E240A, proteolytically inactive MT1-MMP mutant with ala substitution of glu 240 in the catalytic domain. Bottom panel: gelatin zymography. To characterize the proteolytic activity of the various forms of MT1-MMP the transfectants were analyzed for their capacity to activate proMMP-2 as described in Materials and Methods. B. MT1-MMP Tet-Off MCF-7 cell transfectants grown for 24 h in medium containing 0.5% FBS were treated with FGF-2 (0.75 ng/ml) for 15 min in the presence or absence of Ilomastat (50 μM), an MMP inhibitor. Tubulin (TUB) is shown as a loading control. The lower panels of A and B show mean ± S.E. of densitometric readings normalized to the corresponding loading control; *, p ≤ 0.05; control and E240A transfectants + FGF-2 vs. wt, Δpex and Δcyt transfectants + FGF-2. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results.