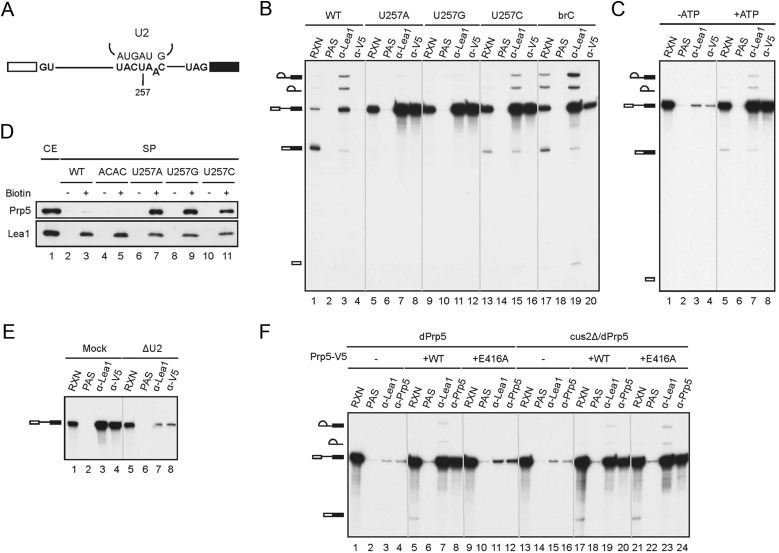
Figure 2.
Stable association of Prp5 with the U257m spliceosome. (A) A diagram showing the sequence of the branch site and the position of the U257 mutation. (B) Splicing reactions were performed in Prp5-V5 extracts with wild-type and U257A, U257G, U257C, and brC mutant pre-mRNAs, and the reaction mixtures were immunoprecipitated with anti-Lea1 or anti-V5 antibody. (RXN) One-tenth of the reaction mixture; (PAS) protein A-Sepharose. (C) Splicing reactions were assembled with U257C mutant pre-mRNA in Prp5-V5 extracts in the presence of glucose (lanes 1–4) or ATP (lanes 5–8), and the reaction mixtures were immunoprecipitated with anti-Lea1 or anti-V5 antibody. (RXN) One-tenth of the reaction mixture; (PAS) protein A-Sepharose. (D) The spliceosome formed with biotinylated wild-type (lane 3), ACAC (lane 5), or U257m (lanes 7,9,11) pre-mRNA in Prp5-V5 extracts was isolated by precipitation with streptavidin-Sepharose, and the components were analyzed by Western blotting. (E) Splicing reactions were carried out in mock-depleted (lanes 1–4) or U2-depleted (lanes 5–8) Prp5-V5 extracts with U257G pre-mRNA. The reaction mixtures were immunoprecipitated with anti-Lea1 or anti-V5 antibody. (F) Splicing reactions were performed with U257G pre-mRNA in Prp5-depleted (lanes 1–12) or Prp5-depleted (lanes 13–24) cus2∆ extracts without (lanes 1–4,13–16) or with (lanes 5–8,17–20) the addition of wild-type Prp5 or the prp5-E416A mutant (lanes 9–12,21–24). The reaction mixtures were immunoprecipitated with anti-Lea1 or anti-V5 antibody. (RXN) One-tenth of the reaction mixture; (PAS) protein A-Sepharose.