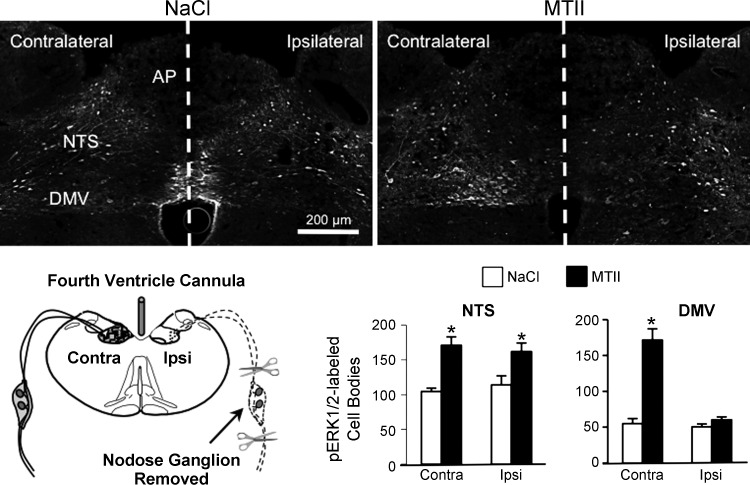
Fig. 6.
MTII-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the NTS and DMV following unilateral nodose ganglion removal and destruction of vagal afferent endings in the ipsilateral hindbrain. Top: representative immunofluorescent images of pERK1/2 immunoreactivity 30 min after fourth ventricle injection of saline (left) or MTII (50 pmol, right) in rats that had undergone unilateral nodose ganglion removal. Schematic in bottom panel illustrates surgical removal of a nodose ganglion and degeneration of central vagal afferent endings in the ipsilateral but not contralateral hindbrain of fourth ventricle-cannulated rats. Bar graph illustrates numbers of pERK1/2-immunoreactive neurons in the NTS and DMV ipsilateral and contralateral to nodose ganglion removal. *Significantly different (P ≤ 0.05) from saline control treatment.