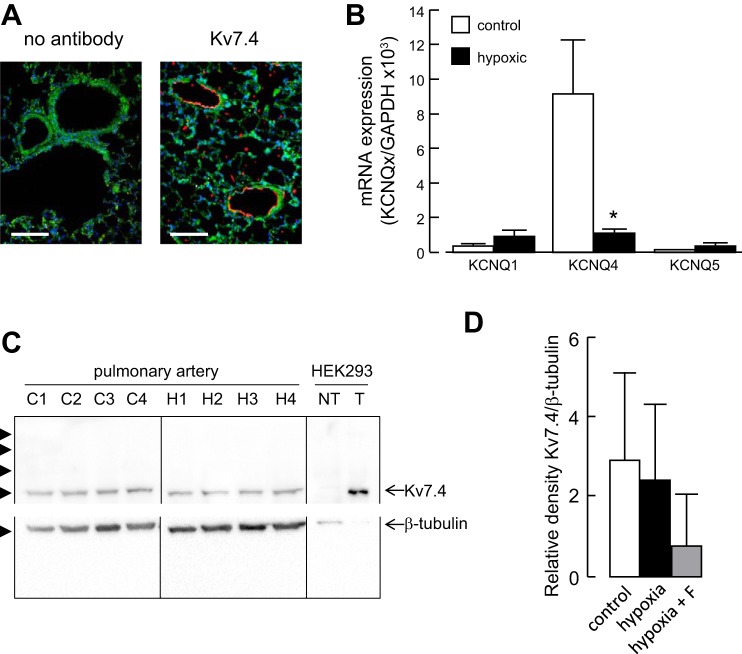
Fig. 5.
Hypoxia downregulates Kv7.4 mRNA expression. A: fluorescence images of lung sections from normoxic rats showing autofluorescence (green) and labeling with an anti-Kv7.4 antibody (red) and the nuclear marker 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Sections were treated identically, except for omission of the Kv7.4 antibody in the control. Calibration bars 100 μm. B: expression profile of KCNQ1, KCNQ4, and KCNQ5 subunit mRNAs in rat pulmonary artery from rats maintained in a normoxic (control) or hypoxic environment for 3 days. Detected with quantitative RT-PCR and normalized to the expression of GAPDH (n = 3). *P < 0.05 hypoxic vs. control. C: Western blots of pulmonary artery proteins from 5 separate normoxic (C1–C4) and hypoxic (H1–H4) rats and proteins from nontransfected HEK-293T cells (NT) and HEK-293T cells overexpressing Kv7.4 channels (T). Proteins were separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane, which was cut between the 50 and 75 kDa markers and probed separately with antibodies against Kv7.4 and β-tubulin. Arrowheads indicate the positions of molecular weight markers (kDa). D: densitometric analysis of Western blots showing Kv7.4 expression normalized to β-tubulin in arteries from normoxic (control) and hypoxic rats, as well as rats administered flupirtine (F, 30 mg/kg/day) and exposed to hypoxia for 5 days (n = 4).