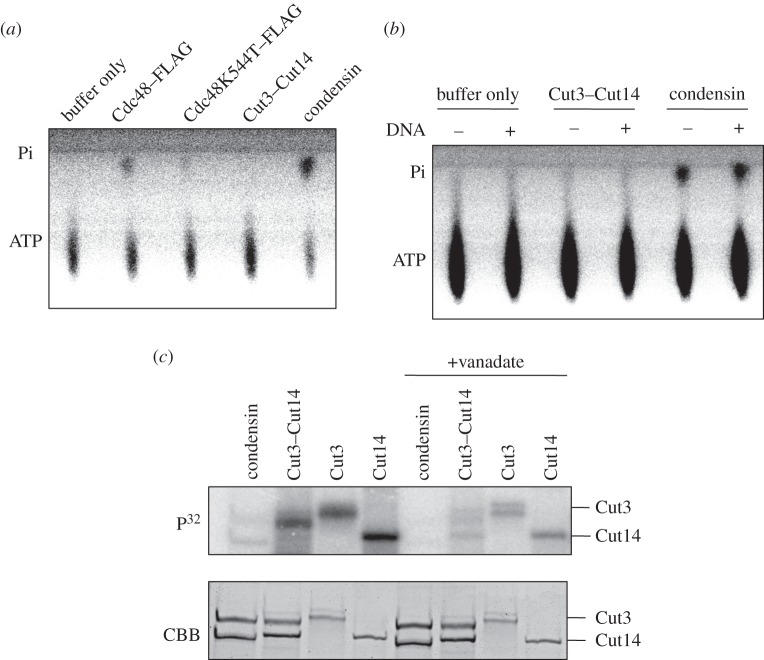
Figure 4.
The relationship of ATPase with, and the effect of vanadate on phosphorylation. (a) Schizosaccharomyces pombe holocondensin employed in this study showed ATPase activity comparable to that of CDC48 ATPase. Activity was detected autoradiographically on thin-layer plates by the release of radiolabelled γP32 (Pi) after incubation of condensin with γP32-ATP. For positive and negative controls, purified Cdc48/p98 and its ATPase-diminished mutant K544T [21], respectively, were employed. Using the same amount of protein (1 μg), the amount of γP32 released by purified condensin was higher than that released by wild-type Cdc48. γP32 release was not detected with purified Cut14/SMC2–Cut3/SMC4, however. (b) Condensin ATPase activity detected in thin-layer chromatography as the release of radioactive γP32 was examined in the presence (+) or the absence (−) of M13 ssDNA (25 ng). Incubation with DNA was for 20 min at 30°C, after which protein was incubated with ATP for 10 min at 30°C. (c) (Left four lanes) Purified single SMC (His-tagged Cut3-H or Cut14-H), double SMC (Cut3–Cut14-H) and heteropentameric holocondensin were incubated in the presence of radiolabelled γP32-ATP (cold ATP 500 nM, hot ATP 41 nM), and run in 6% SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. CBB-stained protein bands are shown below. Single subunits were intensely γP32 labelled due to self-phosphorylation. Weak bands were produced for condensin corresponding to Cut3 and Cut14. (Right four lanes) Vanadate (5 mM) is an ATPase inhibitor.