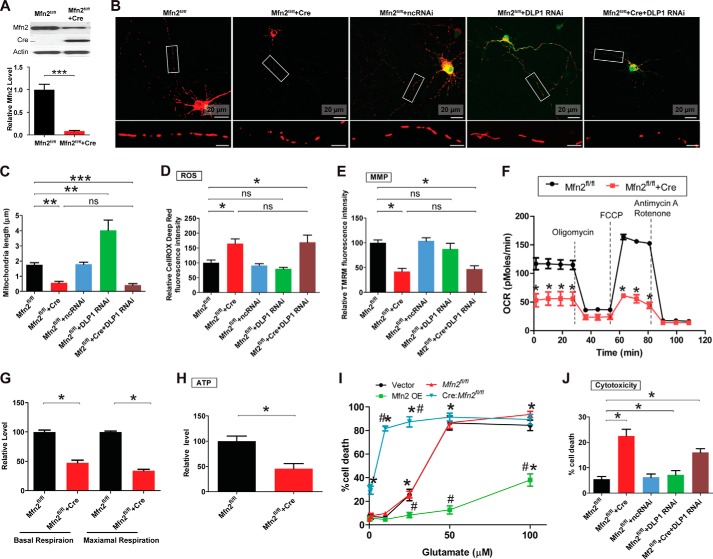
FIGURE 2.
MFN2 deficiency impairs mitochondrial dynamics and function in primary spinal cord motor neurons. To generate MFN2 deficiency neurons, primary mouse motor neurons (Mfn2fl/fl neurons) isolated from Mfn2 floxed mice were transfected with Cre only, GFP-Cre, or mitoDsRed2-Cre or were infected with lentivirus encoding mitoDsRed2 and Cre. Neurons were also transfected/co-transfected with GFP-tagged miR RNAi construct to knock down DLP1 at a 9:1 ratio (Cre construct/GFP-RNAi construct, the 9:1 ratio enables that >99% GFP-positive neurons are also Cre-positive). A, representative immunoblot and quantification analysis confirming the reduction of MFN2 in Tg motor neurons by Cre expression. Representative confocal images (B) and quantification (C) of mitochondrial length in mitoDsRed2 positively transfected primary mouse spinal cord motor neurons (DIV8) as shown. Red, mito-DsRed2. More than 50 neurons were analyzed in per group. Measurement of intracellular levels of ROS (D), MMP (E), OCR (F and G), ATP (H), and neuronal death by LDH assays (I) are shown. J, quantification of neuronal death by propidium iodide assays in positively transfected neurons 3 days after transfection. More than 200 neurons were analyzed per group. All experiments were repeated three times. Data are means ± S.E. Statistics: one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. FCCP, carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone; ns, nonsignificant.