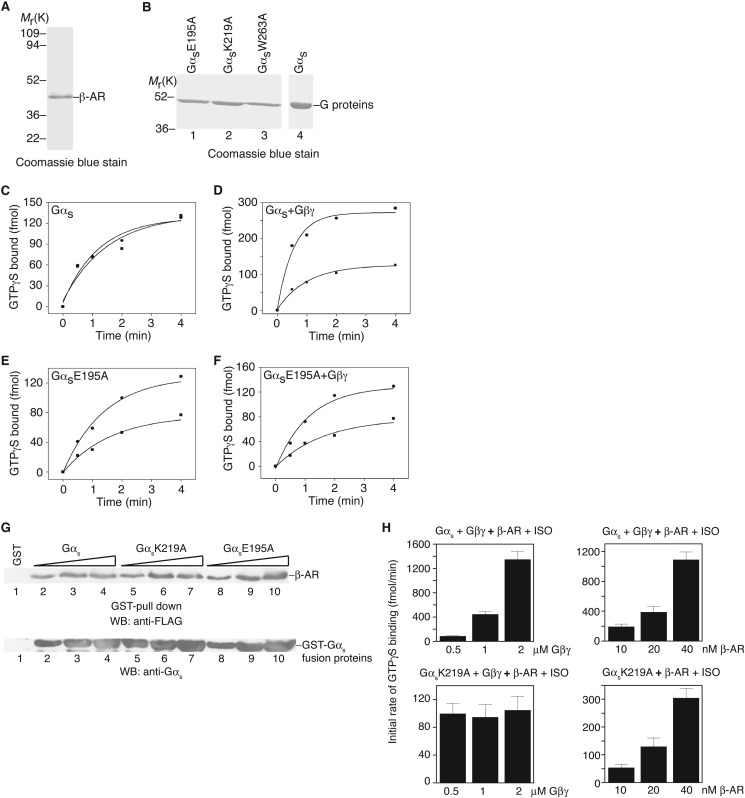
FIGURE 5.
In vitro activation of Gαs by the β-adrenergic receptor. A, Coomassie Blue staining shows the purified turkey β-adrenergic receptor. B, Coomassie Blue staining shows some examples of purified G proteins (after GST cleavage). C, activation of Gαs by the β-adrenergic receptor in the presence of alprenolol (■) or isoproterenol (●). D, activation of Gαs + Gβ1γ2 by the β-adrenergic receptor in the presence of alprenolol (■) or isoproterenol (●). E, activation of GαsE195 by the β-adrenergic receptor in the presence of alprenolol (■) or isoproterenol (●). F, activation of GαsE195 + Gβ1γ2 by the β-adrenergic receptor in the presence of alprenolol (■) or isoproterenol (●). G, in vitro binding of Gαs and representative mutants to β-AR. Different concentrations (150, 300, and 500 nm) of Gαs and mutant proteins were used. H, left two panels, measurement of the initial rate of GTPγS loading onto wild-type Gαs (top panel) or GαsK219A mutant (bottom panel) in the presence of different concentrations of Gβ1γ2. Right two panels, measurement of the initial rate of GTPγS loading onto wild-type Gαs in the presence of Gβ1γ2 (top panel) or the GαsK219A mutant (bottom panel) in the absence of Gβ1γ2. One representative experiment from three independent experiments is shown for A-G. In H, data are shown as mean ± S.E.