FIGURE 3.
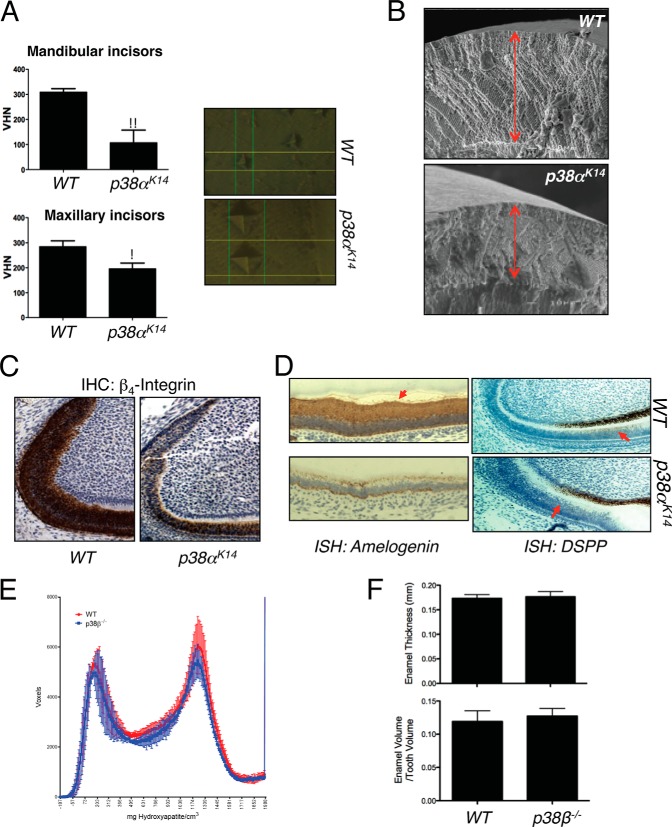
Defects in dental enamel production and ameloblast activity in p38αK14 mice. A, nanoindentation studies of incisors from 6-week-old p38αK14 and WT mice showing decreased enamel hardness, both by quantitative measure (left panels) and by visualization of the probe indentation site (right panels). ** indicates p < 0.01 by a two-tailed unpaired Student's t test; * indicates p < 0.05. VHN, Vickers hardness number. B, scanning electron microscopy analysis of mandibular incisors from 6-week-old p38αK14 and WT mice showing decreased thickness of the enamel layer (red arrows). Bar, 100 μm. C, immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for β4-integrin on mandibular incisors from 4-day-old WT and p38αK14 mice. D, in situ hybridization (ISH) for amelogenin and DSPP on mandibular incisors from 4-day-old WT and p38αK14 mice. The region of DSPP expression in ameloblasts is indicated with a red arrow. E, histogram plotting density on the x-axis versus the volume in voxels corresponding to that density in mandibular incisors from 4-week-old p38β−/− and WT mice. F, quantitation of enamel thickness and enamel volume relative to total tooth volume in the mandibular incisors of 4-week-old p38β−/− and WT mice.