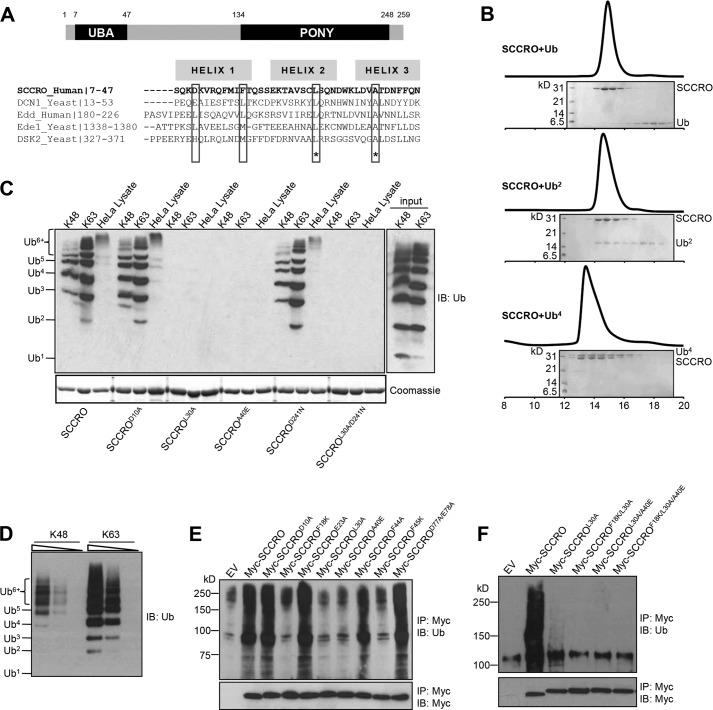
FIGURE 1.
The UBA domain of SCCRO binds polyubiquitin chains in a linkage-independent manner. A, schematic depiction of the domain structure of SCCRO (top panel) and sequence analysis of the UBA domain of SCCRO with several other UBA and CUE domains (bottom panel). Highlighted are conserved hydrophobic residues critical for binding to ubiquitinated proteins. B, SCCRO preferentially binds Ub4 over Ub or Ub2. Lys48-linked ubiquitin chains (Ub2 and Ub4) were synthesized in vitro. Pictured is a size exclusion chromatogram showing that SCCRO was co-eluted with Ub4 but not with Ub or Ub2. C, pulldown assay using GST-SCCRO and its mutants on Lys48 or Lys63 ubiquitin chains or HeLa cell lysates followed by Western blot analysis for ubiquitin showing that SCCRO binds to the ubiquitin chain in a linkage-independent manner. D, pulldown assay using GST-SCCRO on serially diluted Lys48 or Lys63 ubiquitin chains showing that SCCRO has preferential binding toward Lys63-linked ubiquitin chains. E and F, immunoblot (IB) analysis of lysates from U2OS cells transfected with MYC-SCCRO and selected mutants probed with antibody against ubiquitinated proteins following immunoprecipitation (IP) for MYC showing that conserved hydrophobic residues in the UBA domain of SCCRO are critical for binding to ubiquitin chains. EV, empty vector.