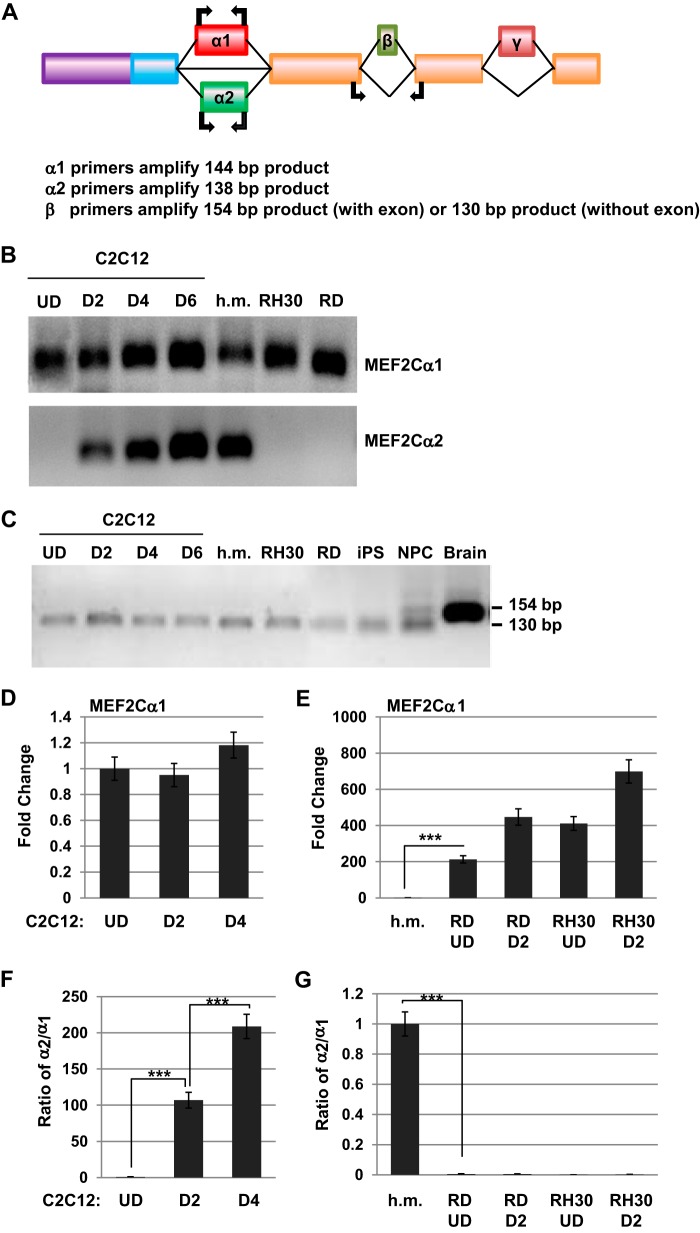
FIGURE 2.
Expression of the α and β exons of MEF2C in normal muscle and RMS. A, schematic of the exon structure of MEF2C with the location of the primers used to detect the indicated exons. B, the α1 exon of MEF2C is expressed ubiquitously in skeletal muscle, but the α2 exon is strongly up-regulated during differentiation. Exon expression was detected by RT-PCR on the indicated samples. U.D., undifferentiated myoblasts; D, days of differentiation; h.m., human myoblasts. C, the β exon is not expressed in muscle or RMS cells. Exon expression was detected by RT-PCR on the indicated samples as in B and from iPS cells, neural progenitor cells (NPC), and brain. D, expression of the α1 exon does not change during myoblast differentiation. Gene expression was assayed by qRT-PCR. Error bars show mean ± S.D. E, the α1 exon is highly expressed in RMS cells, as assayed as in D. ***, p < 0.001. F, the α2 exon is up-regulated during differentiation, as assayed as in D. Data are shown as the ratio of α2 expression relative to the expression of α1. ***, p < 0.001. G, the α2 exon is highly down-regulated in RMS and not induced by differentiation, as assayed as in F. ***, p < 0.001.