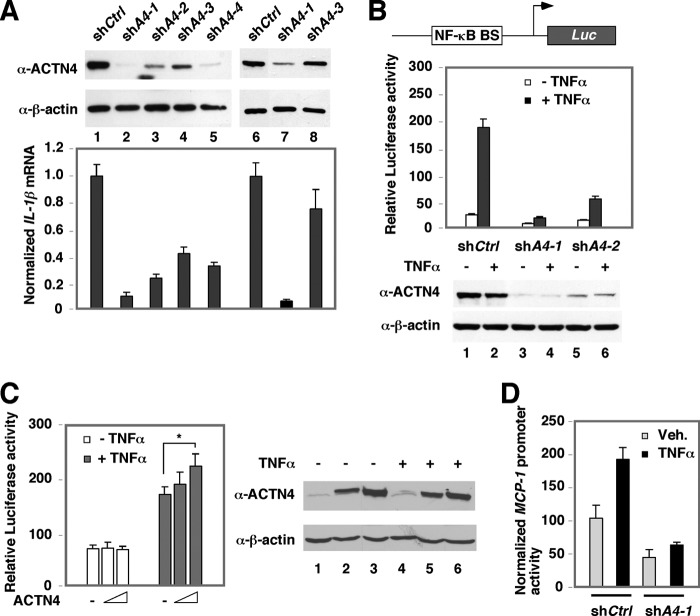
FIGURE 1.
The effect of ACTN4 knockdown on NF-κB-mediated transcriptional activation. A, ACTN4 was stably knocked down by several short hairpin (sh) RNAs (shA1–4) targeting different regions of ACTN4 mRNA in HEK293T cells (lanes 1–5) or HPCs (lanes 6–8). A control shRNA (shCtrl) was used for comparison. The mRNA expression levels of IL-1β of corresponding cells are shown. B, control and ACTN4 stably knockdown HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with a plasmid constitutively expressing β-galactosidase and an NF-κB luciferase (Luc) reporter plasmid. NF-κB BS: NF-κB-binding site. Following transfection, cells were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 12 h, and luciferase activity was measured. A schematic representation of the reporter construct (top) and the expression of ACTN4 (bottom) are shown. C, HEK293T cells were cotransfected with an NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmid and increasing amounts of HA-ACTN4 expression plasmid followed by treatment with vehicle or TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 12 h, and luciferase activity was measured. B and C, the relative luciferase activity was normalized to β-galactosidase activity (*, p < 0.05). D, the MCP-1 promoter reporter construct and CMX-β-gal expression plasmid were transiently transfected into shCtrl or shA4-1 HEK293T cells, treated with or without TNFα, and the reporter activity was assayed. Veh., vehicle. Error bars indicate mean ± S.D.