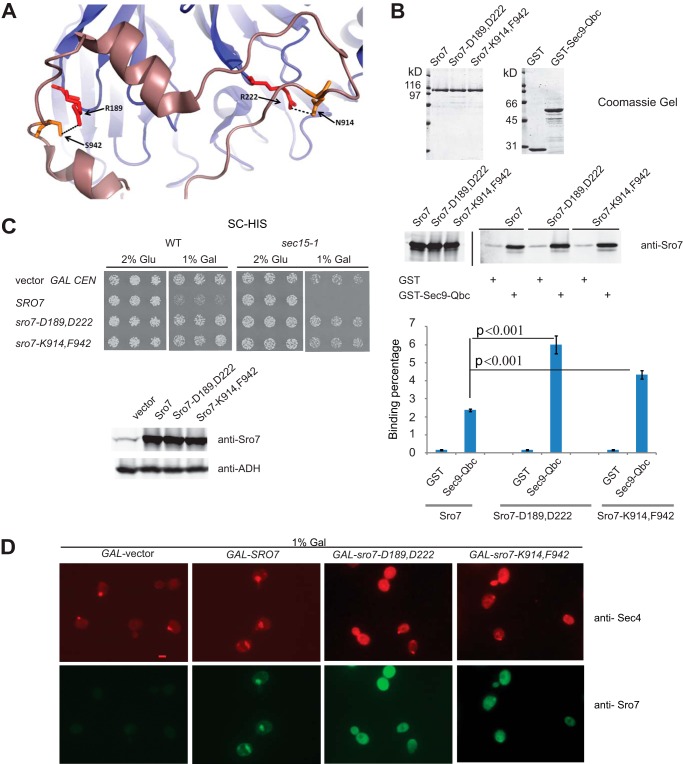
FIGURE 7.
Sro7-N914K,S942F behaves genetically and biochemically like sro7-R189D,R222D. A, schematic structure of Sro7 illustrating hydrogen bonds between R189,R222 on the N-terminal propeller of Sro7 and N914,S942 on the C-terminal tail. B, wild type and mutant Sro7 proteins were purified and analyzed for binding to the Sec9-Qbc domain as described previously. Standard Student's t test showed a p value of <0.001. C, wild type and sec15-1 mutant strains were transformed with plasmids (CEN) overexpressing SRO7, sro7-D189,D222 and sro7-K914,F942 from a GAL promoter. Three individual colonies were picked and transferred to selective media in the presence of glucose or galactose. Equal absorbance units of the strains induced in galactose were harvested, washed in Tris (10 mm) and azide (20 mm), and lysed by glass bead lysis before subjecting to Western blot analysis. D, wild type cells containing plasmids expressing Sro7, or mutant proteins from a GAL-inducible promoter (CEN), or vector only were grown in selective media and induced for 6 h in galactose before fixing and processing for immunofluorescence analysis using monoclonal Sec4 and polyclonal Sro7 antibodies. Scale bar, 2 μm.