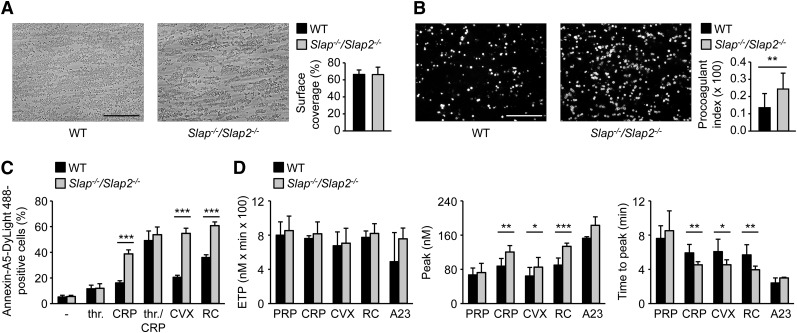
Figure 4.
SLAP/SLAP2 deficiency enhances procoagulant activity and (hem)ITAM-dependent thrombin generation in platelets. (A) Unaltered surface coverage by collagen-adherent platelets in WT and Slap−/−/Slap2−/− blood. Representative phase-contrast images are depicted. (B) Increased PS exposure of Slap−/−/Slap2−/− platelets, as demonstrated by Annexin-A5-DyLight 488 staining of platelets. Procoagulant index indicates the ratio of surface coverage of PS-exposing platelets (Annexin-A5-DyLight 488 staining of platelets) to the total surface covered by platelets. Results in (A) and (B) are representative of 2 independent experiments with n ≥ 6. Images were obtained at ×40. Bars represent 50 μm. (C) Washed platelets were stimulated with 0.1 U/mL thrombin, 20 μg/mL CRP, a combination of both thrombin and CRP, 1 μg/mL convulxin, or 0.12 μg/mL rhodocytin, stained with saturating amounts of Annexin-A5-DyLight 488, and directly analyzed by flow cytometry. Results are representative of 2 independent experiments with n = 5. (D) Citrate-anticoagulated PRP was left unstimulated, or platelets were activated by incubation with convulxin (1 μg/mL), CRP (20 μg/mL), rhodocytin (1 μg/mL), or the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 (A23) (10 μM) for 10 minutes at 37°C. Thrombin generation was triggered with tissue factor/CaCl2. Endogenous thrombin potential (left); quantification of thrombin peak height (middle); and quantification of time to peak (right). n = 3 for A23187; n = 7 for CRP and RC; and n = 10 for PRP and CVX. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001. A23, A23187; CRP, collagen-related peptide; CVX, convulxin; ETP, endogenous thrombin potential; PRP, platelet-rich plasma; RC, rhodocytin; thr., thrombin.