Figure 4.
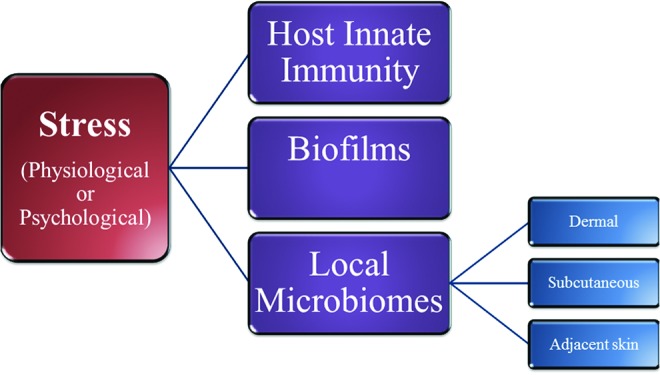
Stress mediators influence the wound microbiome. Stress mediators (i.e., cortisol, catecholamines, acetylcholine, neuropeptides, etc.) directly promote alterations in the host innate immune response, the formation of biofilms, and the formation/dynamics of the various skin microbiomes. The interplay between these factors ultimately determines both the composition of the wound microbiome, as well as the stagnation or progression of wound healing responses.9,17,20,35,53,63,67,68 To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/wound
