Figure 2. CCR2-deficient mice fail to recruit GIMs to the K1492 tumour before or after Myxoma treatment.
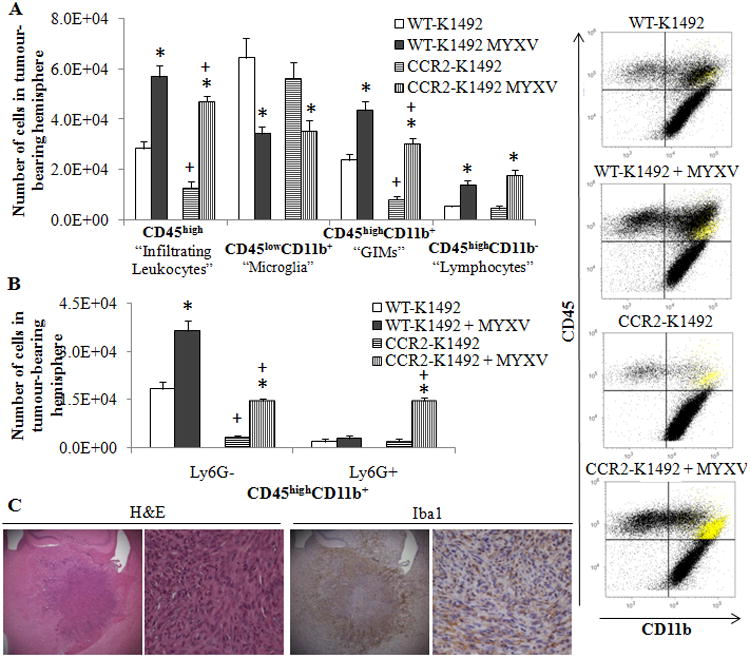
Wildtype (WT) or CCR2-deficient (CCR2) C57Bl/6 mice implanted with K1492 cells and analyzed by flow cytometry at 15 days-post implantation, 3 days post-treatment with Myxoma virus (5×106 FFU vMyx-GFP) or untreated. A - Quantified numbers of each cell type isolated from the tumour-bearing hemisphere (Left; n=6) accompanied by representative CD45/CD11b scatter plot (right). Highlighted in yellow are the Ly6G+ granulocytes. B – Addition of the Ly6G antibody to the flow cytometry analysis demonstrates granulocytic recruitment in MYXV-treated animals and refines the GIM classification of our data (n =3). Error bars represent standard error and asterisks represent significant differences within mouse strain but between treatment groups. Plus signs represent significant differences between mouse strains within treatment groups (p<0.05); there is no significant difference between WT-K1492 and CCR2-K1492 MYXV for GIMs. C - K1492-bearing CCR2-deficient mice were harvested at 14 days post-injection for formalin-fixed paraffin sections (Top row 25×; Second row 200X). Representative staining from 3 animals/group.
