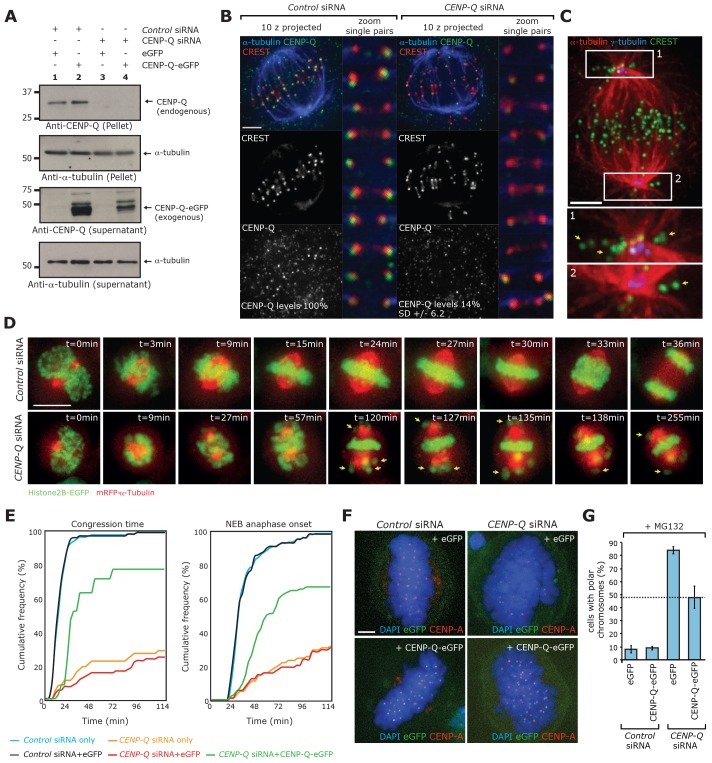
Fig. 1.
Depletion of the outer-plate protein CENP-Q causes accumulation of polar chromosomes. (A) Immunoblots of whole-cell HeLa E1 lysates that had been transfected with control siRNA or an siRNA against CENP-Q (CENP-Q siRNA) for 12 h and then transfected with either empty vector or an siRNA-resistant vector expressing CENP-Q tagged with eGFP for 48 h. The blot was probed with antibodies against CENP-Q and α-tubulin. Endogenous CENP-Q and the corresponding α-tubulin control are shown in the top two panels. The pellet fraction is shown as nonspecific staining obscuring the protein in the supernatant. Expression of the transgene and corresponding α-tubulin loading control are shown in the lower two panels. (B) Immunofluorescence microscopy images of metaphase cells and magnified (zoom) kinetochore pairs in cells transfected with a control siRNA or CENP-Q siRNA that were then stained with CREST antisera (red) and antibodies against CENP-Q (green) and α-tubulin (blue). The images of metaphase cells correspond to z-projections (10 focal planes at 0.2 µm spacing) and the zoom images of the single kinetochores are from a single focal plane of the stack. Values at the base of the bottom two panels correspond to the relative values of CENP-Q staining in control and CENP-Q-depleted cells (n = 3, 150 kinetochores, 30 cells). (C) Immunofluorescence microscopy images of a CENP-Q-depleted metaphase HeLa E1 cell stained with CREST antisera (green) and an antibody against α-tubulin (red). The image is a z-projection (10 focal planes at 0.2 µm spacing). Zoom boxes 1 and 2 are centred on the spindle poles, and yellow arrows point to unaligned kinetochores around the spindle poles. (D) Frames from live-cell movies of HeLa E1 cells co-expressing H2B–eGFP and mRFP–α-tubulin in control (top row) and CENP-Q-siRNA-treated cells (second row). Yellow arrows point to unaligned kinetochores. Videos of control and CENP-Q-depleted cells are available in in supplementary material Movies 1 and 2, respectively. t = 0, point of nuclear envelope breakdown. (E) Quantification of the time from nuclear envelope breakdown (NEB) to the time when the last chromosome congressed to the metaphase plate, and NEB to the time of anaphase onset. Blue and orange lines indicate the timings of HeLa E1 cells co-expressing H2B–eGFP and mRFP–α-tubulin in control and CENP-Q-siRNA-treated cells, respectively. Black green and red lines represent timing data from cells expressing H2B–mRFP that had been treated with control siRNA and siRNA-resistant CENP-Q–eGFP vector (black), CENP-Q siRNA and siRNA-resistant CENP-Q–eGFP vector (green) and CENP-Q siRNA and eGFP vector (red). (F) Immunofluorescence microscopy images (z-projections, 10 focal planes at 0.2 µm spacing) of a CENP-Q-siRNA rescue experiment in HeLa E1 cells. Cells were treated with CENP-Q siRNA or control siRNA for 14 h and then transfected with an siRNA-resistant CENP-Q–eGFP construct or a control eGFP expression plasmid for a further 48 h. To reduce the effect of the mitotic stage on alignment, cells were treated with 1 µM MG132 for 90 min before fixation. Cells were stained with DAPI and probed with an antibody against CENP-A. (G) Quantification of cells with polar chromosomes in the rescue experiment described in F. n = 2, ≥100 poles, 50 cells. Scale bars: 3 µm (B,C,F); 10 µm (D).