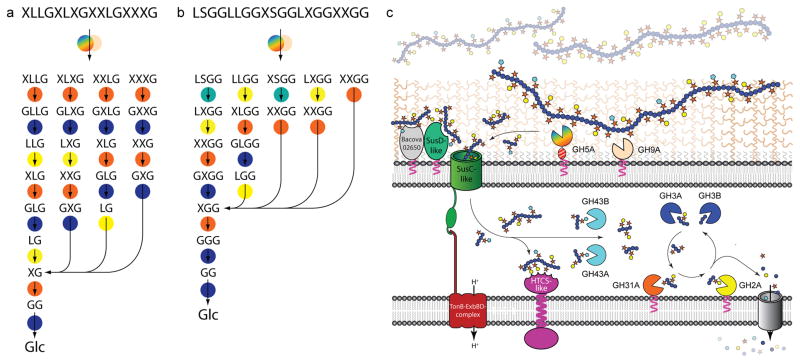
Figure 3.
The concerted action of XyGUL gene products in the degradation of xyloglucans. Most probable sequential pathways for the hydrolysis of (galacto)xyloglucan (a) and (arabinogalacto)xyloglucans (b) based on enzyme kinetic data, product analysis, and selected gene knock-out studies (see Fig. 1 for XyG motif abbreviations). Enzymes are represented as circles, colour-coded as in panel c: Rainbow, endo-xyloglucanase BoGH5A; tan, endo-xyloglucanase BoGH9A; orange, α-xylosidase BoGH31A; turquoise α-L-arabinofuranosides BoGH43A and/or BoGH43B; yellow β-galactosidase BoGH2; dark blue β-glucosidases BoGH3A and/or BoGH3B. c. Model of enzyme localisation by analogy with the archetypal Sus locus4 and based on inference of N-terminal lipoprotein modification from protein sequence data.